目录
- 使用psycopg2插件
- psycopg2插件使用
- 1、python更新pip插件
- 2、Python安装psycopg2插件
- 3、信任该安装源
- 1.4、Python安装chardet插件
- 5、查看已安装的插件pip list
- 6、创建Python文件
- 7、创建Python文件
- 8、创建测试SQL脚本
- 9、执行execute_db_script.py
- 10、查看数据库
使用psycopg2插件
psycopg2插件简介
psycopg2库介绍: Psycopg2是一个用于Python编程语言的第三方库,用于访问PostgreSQL数据库系统。它提供了一组工具和方法,可以轻松地在Python程序中进行数据库操作,包括查询、插入、更新、删除等操作。
以下是Psycopg2库的一些主要特点:
1.简单易用:Psycopg2提供了简单的API,易于学习和使用。
2.高性能:Psycopg2是基于C语言实现的,能够提供高效的数据库操作。
3.完全兼容:Psycopg2与PostgreSQL数据库完全兼容,并支持大多数PostgreSQL特性。
4.安全性:Psycopg2具有内置的防止SQL注入攻击的功能,能够保证数据安全。
5.使用Psycopg2库进行数据库操作通常需要以下步骤:
- 安装psycopg2库:可以使用pip install psycopg2来安装该库。
- 建立数据库连接:使用psphpycopg2库提供的connect()方法建立与数据库的连接。
- 执行SQL语句:使用psycopg2提供的方法执行SQL语句,如查询、插入、更新等操作。
- 处理查询结果:如果执行的是查询操作,需要使用fetchone()或fetchall()方法来处理查询结果。
- 关闭连接:最后需要使用close()方法关闭数据库连接。
psycopg2插件使用
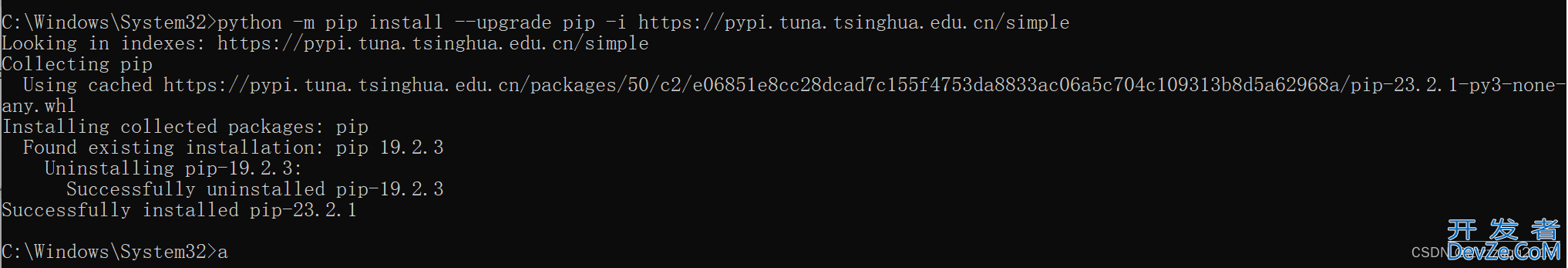
1、Python更新pip插件
以管理员权限打开命令行窗口,执行下面的命令:
python -m pip install --upgrade pip -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
2、Python安装psycopg2插件
以管理员权限打开命令行窗口,执行下面的命令:
pip install psycopg2 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
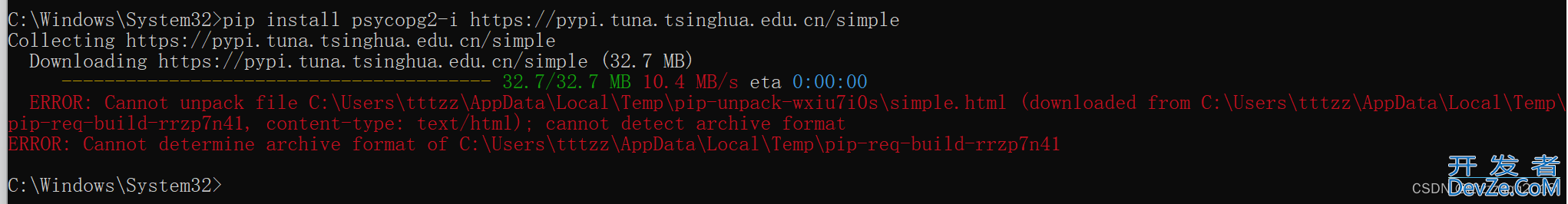
报错:ERROR: Cannot determine archive format of C:\Users\tttzz\AppData\Local\Temp\pip-req-build-rrzp7n41
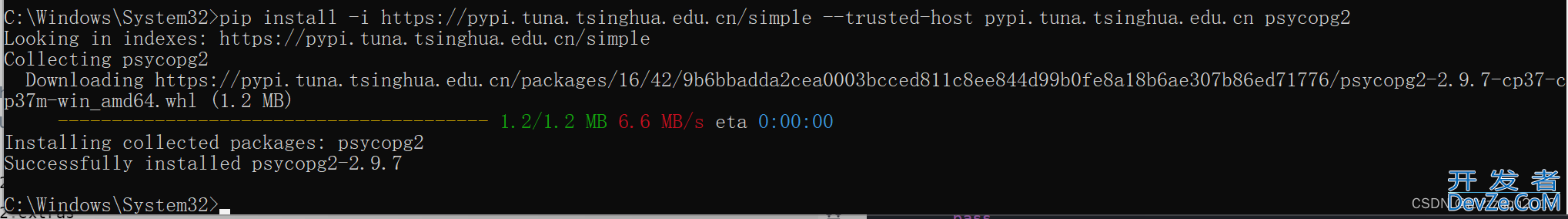
3、信任该安装源
以管理员权限打开命令行窗口,执行下面的命令:
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple --trusted-host pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn psycopg2
1.4、Python安装chardet插件
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple --trusted-host pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn chardet

PyCharm下安装chardet插件,安装完毕。
5、查看已安装的插件pip list
pip list
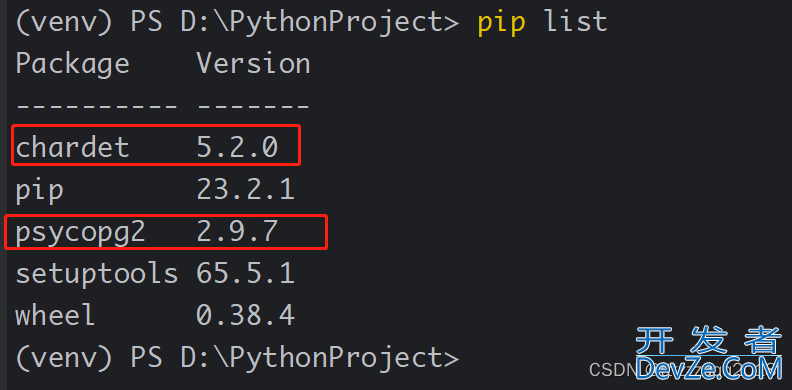
从上面的清单,发现插件chardet及psycopg2都安装成功了,下面开始php来创建Python文件来对PostgreSQL数据库进行操作。
6、创建Python文件
PostgreSQLExecuteSql.py
上代码:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import chardet
import psycopg2
import psycopg2.extras
class PostgreSQLExecuteSql:
"""
Python Test Library for TZQ
"""
def __init__(self):
pass
def get_encoding(self, file):
# 获取文件编码类型
# 二进制方式读取,获取字节数据,检测类型
with open(file, 'rb') as f:
return chardet.detect(f.read())['encoding']
# 输出文件所有内容
def get_file_content1(self, file_path):
# filePath="d:/20220711-1657.sql"
file_encoding = self.get_encoding(file_path)
# print(get_encoding(filePath))
file = open(file_path, "r", encoding=file_encoding)
# print(file.read())
str = file.read()
file.close()
return str
# 按行输出文件内容
def get_file_content2(self, filePath):
# filePath="d:/20220711-1657.sql"
file_encoding = self.get_encoding(filePath)
print(self.get_encoding(filePath))
file = open(filePath, "r", encoding=file_encoding)
# print(file.readline())
str = file.readline()
file.close()
return str
# for循环读取文件内容
def get_file_content3(self, filePath):
with open(filePath, "r", encoding=self.get_encoding(filePath)) as file:
for item in file:
print("file_content:" + item)
# conn = psycopg2.connect("dbname=tzqlog_pro user=tzq password=Tzq@123456 host=127.0.0.1 port=5432")
# 连接数据库执行脚本
def conn_db_exec_sql(self, sql_script, dbname, user, password, host, port):
connect_string = "dbname=" + dbname + " user=" + user + " password=" + password + " host=" + host + " port=" + port
print(connect_string)
# 连接到数据库
conn = psycopg2.connect(connect_string)
# 建立游标,用来执行数据库操作
# 这⾥创建的是⼀个字典Cursor, 这样返回的数据, 都是字典的形式, ⽅便使⽤
# cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor_factory=psycopg2.extras.DictCursor)
# 读取文本文件中的内容
file_content = self.get_file_content1(sql_script)
# 执行SQL命令
cursor.execute(file_content)
# 提交SQL命令
conn.commit()
# 执行SQL SELECT命令
# command = 'SELECT * FROM test_conn '
# cursor.execute(command)
## 获取SELECT返回的元组
# rows = cursor.fetchall()
# 关闭数据库连接
conn.close()
# print(rows)
"""TZQLOG"""
# 连接数据库执行脚本 - TZQLOG PRO 环境
def exec_sql__TZQLOG_DB_PRO(selfphp, sql_script):
# 配置项
dbname = "tzqlog_db_pro"
user = "plan"
password = "Tzq@123456"
host = "127.0.0.1"
port = "5432"
self.conn_db_exec_sql(sql_script, dbname, user, password, host, port)
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# postgreSQLExecuteSql = PostgreSQLExecuteSql()
# # 执行的脚本文件全路径
# sql_file_path = "D:/20220706-1736-tzqlog_XXX.sql"
# # 在 TZQLOG PRO 执行脚本
# postgreSQLExecuteSql.exec_sql__TZQLOG_DB_PRO(sql_file_path)
7、创建Python文件
execute_db_script.py
上代码:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import PostgreSQLExecuteSql # from PostgreSQLExecuteSql import PostgreSQLExecuteSql # import sys ''' TZQ 环境 汇总 一套执行 ''' # 执行的脚本文件全路径 # 脚本目录名 DIR_STRING = "D:/oracle_database/sql/" # 脚本文件名 # FILE_NAME = "2022070php6-1736-tzq-xxxxx.sql" # FILE_NAME = "20220715-1522-张三-xxxx更新.sql" FILE_NAME = "20230822-2312-log创建表-log_test_t.sql" ''' TZQ 环境 汇总 一套执行 ''' # 脚本全路径 sql_file_path = DIR_STRING + FILE_NAME print(sql_file_path) # 定义类的实例 postgreSQLExecuteSql = PostgreSQLExecuteSql.PostgreSQLExecuteSql() # ################################各个环境下执行脚本################################ # 在 “TZQ DEV 环境” 执行脚本 # postgreSQLExecuteSql.exec_sql__TZQLOG_DB_DEV(sql_file_path) # 在 “TZQ PRO 环境” 执行脚本 postgreSQLExecuteSql.exec_sql__TZQLOG_DB_PRO(sql_file_path)
8、创建测试SQL脚本
20230822-2312-log创建表-log_test_t.sql
在 D:/oracle_database/sql/ 目录下创建脚本文件:20230822-2312-log创建表-log_test_t.sql:
create table log_info_t ( info_id INT8 not null, info_type_id INT8, title VARCHAR(200), content TEXT, article_view_count INT8 default 1 not null, created_by INT8 default -1 not null, creation_date TIMESTAMP(0) default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP not null, last_updated_by http://www.devze.com INT8 default -1 not null, last_update_date TIMESTAMP(0) default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP not null, delete_flag VARCHAR(1) default 'N' not null, deleted_by INT8, delete_date TIMESTAMP(0), content_no_html TEXT, info_right VARCHAR(50) default 'all' ); CREATE SEQUENCE log_info_s;
如下图:

脚本内容是创建表和序列。下面我们来执行下Python脚本,看能不能在我们的目标数据库中能够创建表和序列。
9、执行execute_db_script.py
执行完后信息:
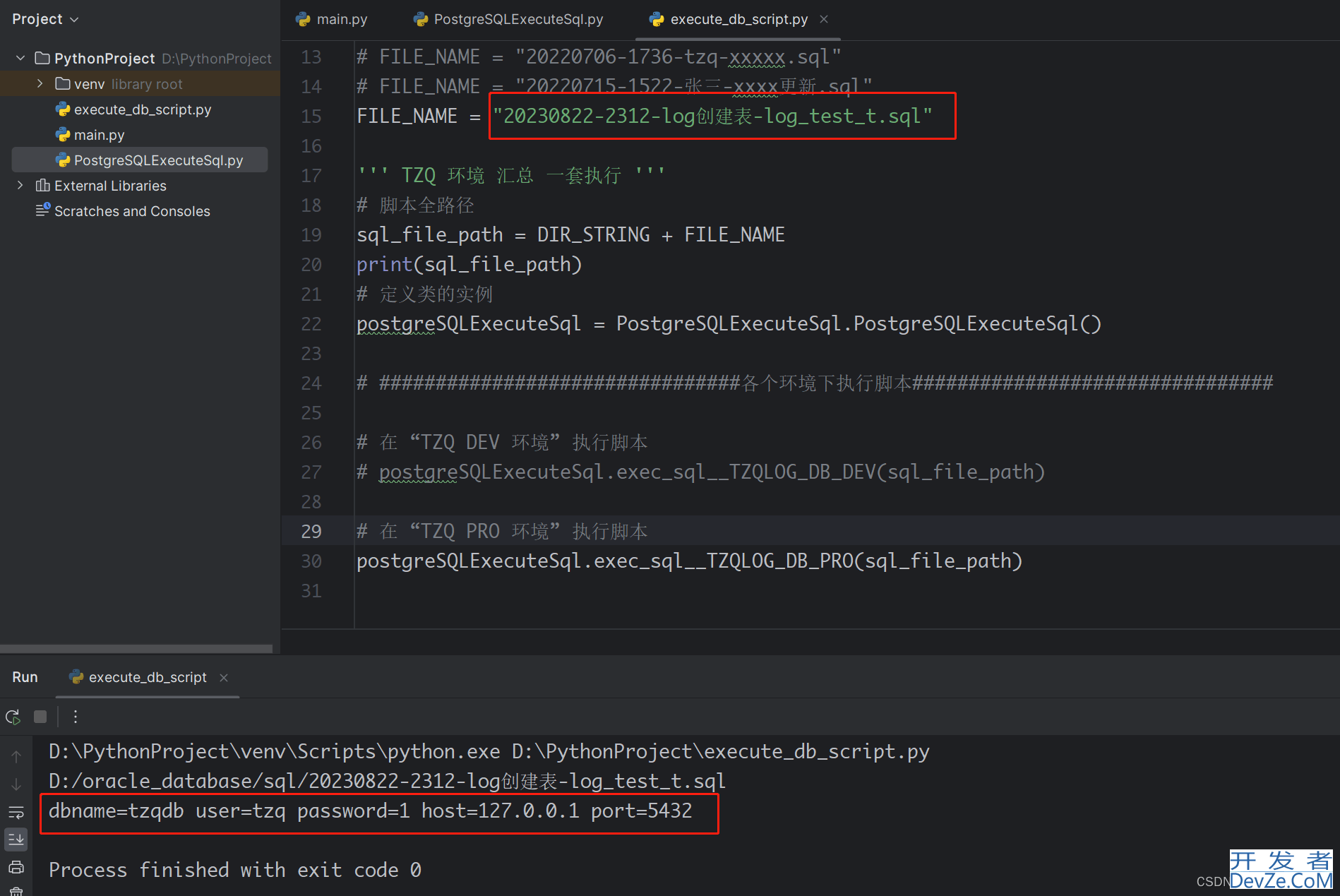
10、查看数据库
查看数据库中,已经有了这个表和序列
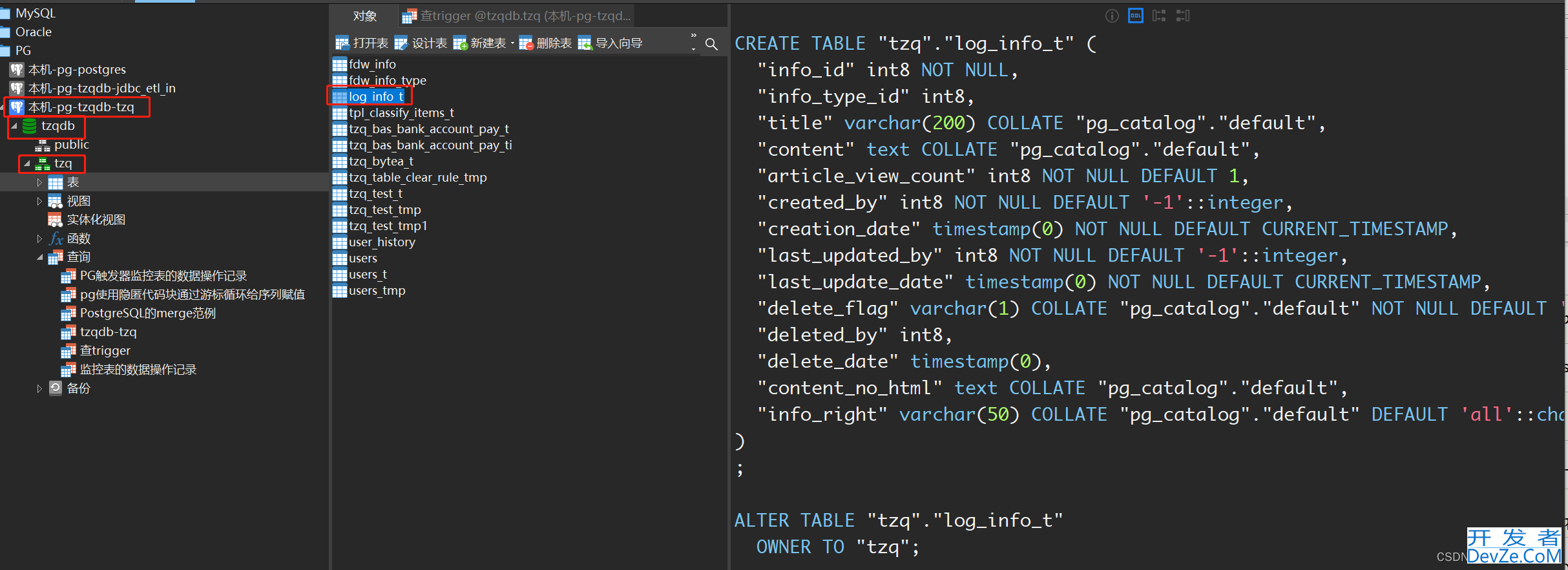
至此。Python执行PostgreSQL数据库的SQL脚本,就为大家演示完毕了!!!
以上就是Python执行PostgreSQL数据库的SQL脚本详解的详细内容,更多关于Python执行PostgreSQL数据库sql脚本的资料请关注编程客栈(www.devze.com)其它相关文章!





 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论