目录
- 一、AOP 与 Spring AOP
- 二、Spring AOP简单实现
- 三、详解Spring AOP
- 3.1 Spring AOP 核心概念
- 3.1.1 切点(Pointcut)
- 3.1.2 连接点(Join Point)
- 3.1.3 通知(Advice)
- 3.1.4 切面(ASPect)
- 3.2 通知类型
- 3.3 公共切点引用@PointCut
- 3.4 切点优先级@Order
- 3.5 切点表达式
- 3.5.1 execution
- 3.5.2 @annotation
一、AOP 与 Spring AOP
AOP:Aspect Oriented Programming(⾯向方⾯编程)。是一种对某一类事情集中处理的思想。
Spring AOP:就是对AOP思想的一种实现。
二、Spring AOP简单实现
我们简单实现一个统计每个接口的用时。
引入依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId> </dependency>
写AOP实现:
- 类使用注解@Aspect修饰
- 方法参数为ProceedingJoinPoint 类,代表要实现的方法(只能在Around通知下写)
- 方法使用注解@Around,参数是对应的路径的切点
- ProceedingJoinPoint 的参数执行proceed方法。
package com.example.library.aspect;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class TimeAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.example.library.controller.*.*(..) )")
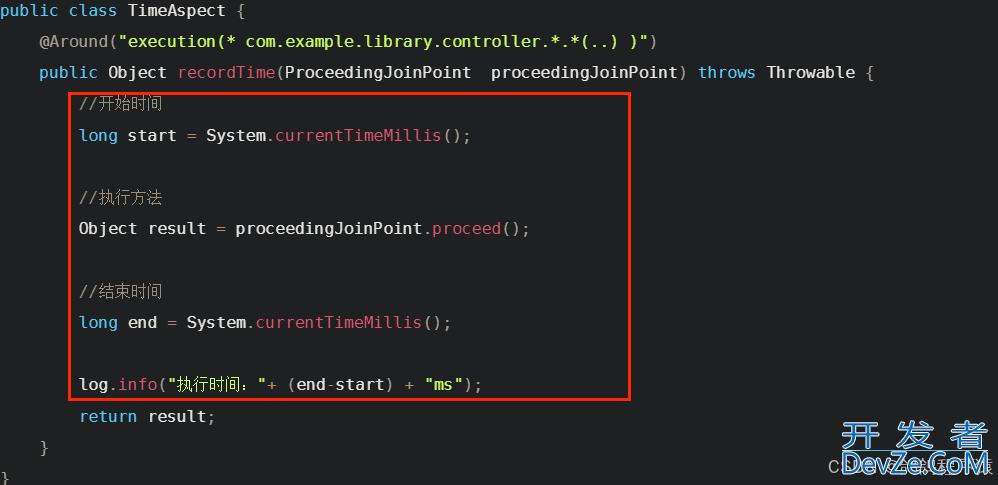
public Object recordTime(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
//开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//执行方法
Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
//结束时间
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("执行时间:"+ (end-start) + "ms");
return resultjavascript;
}
}
三、详解Spring AOP
3.1 Spring AOP 核心概念
Spring AOP 核心概念:切点,连接点,通知,切面。
我们以上面的代码来介绍。
3.1.1 切点(Pointcut)
切点:就是告诉程序哪些方法需要使用到接下来的功能。
上面的@Around注解的参数就是切点表达式。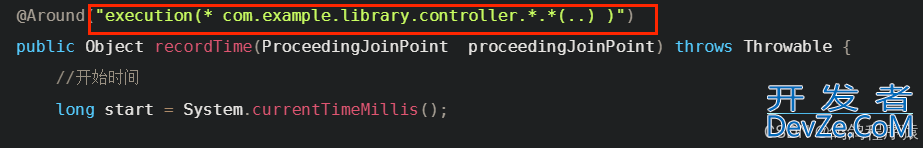
3.1.2 连接点(Join Point)
连接点:满⾜切点表达式规则的⽅法,就是连接点。也就是可以AOP控制的⽅法。
就像上面的代码的连接点就是:com.example.library.controller路径下的所有方法。
切点和连接点的关系:
- 连接点是满⾜切点表达式的元素。
- 切点可以看做是保存了众多连接点的⼀个集合。
3.1.3 通知(Advice)
通知:这个Spring AOP方法要实现的功能就是通知。
就像上面的实现一个统计每个接口的用时的需求,就是通知。
3.1.4 切面(Aspect)
切⾯(Aspect) = 切点(Pointcut) + 通知(Advice)。
通过切⾯就能够描述当前AOP程序需要针对于哪些⽅法,在什么时候执⾏什么样的操作。
切⾯既包含了通知逻辑的定义,也包括了连接点的定义。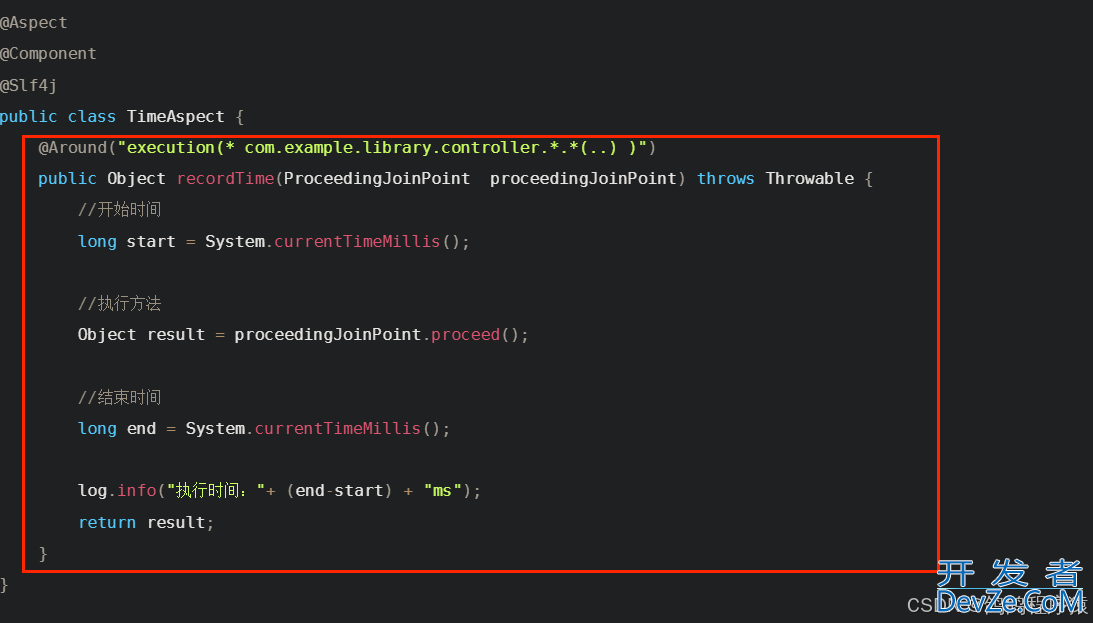
3.2 通知类型
Spring中AOP的通知类型有以下⼏种:
- @Around:环绕通知,此注解标注的通知⽅法在⽬标⽅法前,后都被执⾏。
- @Before:前置通知,此注解标注的通知⽅法在⽬标⽅法前被执⾏。
- @After:后置通知,此注解标注的通知⽅法在⽬标⽅法后被执⾏,⽆论是否有异常都会执⾏。
- @AfterReturning:返回后通知,此注解标注的通知⽅法在⽬标⽅法后被执⾏,有异常不会执⾏。
- @AfterThrowing:异常后通知,此注解标注的通知⽅法发⽣异常后执⾏。
效果:
package com.example.demoaop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Slf4j
@Aspect
public class TestAspect {
//前置通知
@Before("execution(* com.example.demoaop.*.*(..) )")
public void testBefore() {
log.info("Before 方法执行前");
}
//后置通知
@After("execution(* com.example.demoaop.*.*(..) )")
public void testAfter() {
log.info("After 方法执行后");
}
//返回后通知
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.example.demoaop.*.*(..) )")
public void testAfterReturning() {
log.info("AfterReturning 返回后通知");
}
//抛出异常后通知
@AfterThrowing("execution(* com.example.demoaop.*.*(..) )")
public void testAfterThrowing() {
log.info("AfterThrowing 抛出异常后通知");
}
//环绕通知
@Around("execution(* com.example.demoaop.*.*(..) )")
public void testAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
log.info("Around 方法执行前");
Object proceed = pjp.proceed();
log.info("Around 方法执行后");
}
}

3.3 公共切点引用@PointCut
当我们的切点表达式是一样的时候,像上面我们还是在每一个通知类型的注解中,都使用了相同的表达式。
我们就可以使用方法注解@PointCut将切点表达式提取出来,然后后面使用只需要写方法名即可。在其他切点类中也可以调用,需要将@PointCut注解所在类的路径写出来。package com.example.demoaop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Slf4j
@Aspect
public class TestAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.demoaop.*.*(..) )")
public void pc(){}
//前置通知
@Before("pc()")
public void testBefore() {
log.info("TestAspect Before 方法执行前");
}
//后置通知
@After("pc()")
public void testAfter() {
log.info("TestAspect After 方法执行后");
}
}
package com.example.demoaop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Slf4j
@Aspect
public class TestAspect2 {
//前置通知
@Before("com.example.demoaop.TestAspect.pc()")
public void testBefore() {
log.info("TestAspect2 Before 方法执行前");
}
//后置通知
wlTlviCECz @After("pc()")
public void testAfter() {
log.info("TestAspect2 After 方法执行后");
}
}
结果:
可以看见生效了,而且在其他切点类中只有加上了路径的才生效了。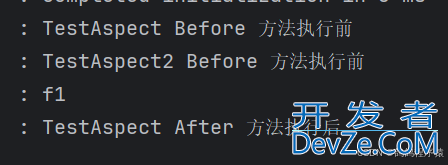
3.4 切点优先级@Order
我们定义3个一样的切点类,看他们的输出顺序:

存在多个切⾯类时,默认按照切⾯类的类名字⺟排序:
- @Before 通知:字⺟排名靠前的先执⾏
- @After 通知:字⺟排名靠前的后执⾏
但这种⽅式不⽅便管理,我们的类名更多还是具备⼀定含义的。
Spring 给我们提供了⼀个新的注解,来控制这些切⾯通知的执⾏顺序:@Order我们将切点类的优先级换一下:
@Component
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Order(1)
pub编程客栈lic class TestAspect3 {
//前置通知
@Before("com.example.demoaop.TestAspect.pc()")
public void testBefore() {
log.info("TestAspect3 Before 方法执行前");
}
//后置通知
@After("com.example.demoaop.TestAspect.pc()")
public void testAfter() {
log.info("TestAspect3 After 方法执行后");
}
}
@Component
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Order(2)
public class TestAspect2 {
//前置通知
@Before("com.example.demoaop.TestAspect.pc()")
public void testBefore() {
log.info("TestAspect2 Before 方法执行前");
}
//后置通知
@After("com.example.demoaop.TestAspect.pc()")
public void testAfter() {
log.info("TestAspect2 After 方法执行后");
}
}
@Component
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Order(3)
public class TestAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.demoaop.*.*(..) )")
public void pc(){}
//前置通知
@Before("pc()")
public void testBefore() {
log.info(编程"TestAspect Before 方法执行前");
}
//后置通知
@After("pc()")
public void testAfter() {
log.info("TestAspect After 方法执行后");
}
}
执行结果:

规律:
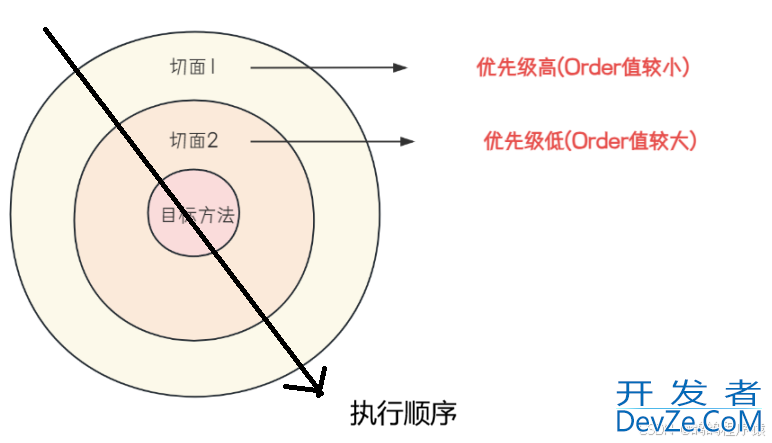
@Order 注解标识的切⾯类,执⾏顺序如下:- @Before 通知:数字越⼩先执⾏
- @After 通知:数字越⼤先执⾏
像下图的表示,箭头代表执行过程:
3.5 切点表达式
切点表达式用来描述切点,常有以下两种类型的切点表达式:execution 和 @annotation
3.5.1 execution
语法:
execution(<访问修饰限定符> <返回类型> <包名.类名.方法名(方法参数)> <异常>)
含义:
- 访问修饰限定符:表示切点对应的方法的访问修饰限定符
- 返回类型:表示切点对应的方法的返回类型
- 包名.类名.方法名(方法参数):表示切点对应的方法的路径及参数
- 异常:表示切点对应的方法抛出的异常
- 访问修饰限定符 和 异常 可以省略
切点表达式⽀持通配符表达:
:* 匹配任意字符,只匹配⼀个元素(返回类型,包,类名,⽅法或者⽅法参数)
1.1. 包名使⽤ * 表⽰任意包(⼀层包使⽤⼀个 * )1.2. 类名使⽤ * 表⽰任意类1.3. 返回值使⽤ * 表⽰任意返回值类型1.4. ⽅法名使⽤ * 表⽰任意⽅法1.5. 参数使⽤ * 表⽰⼀个任意类型的参数: 两个点 . . 匹配多个连续的任意符号,可以通配任意层级的包,或任意类型,任意个数的参数2.1. 使⽤ . . 配置包名,标识此包以及此包下的所有⼦包2.2. 可以使⽤ . . 配置参数,任意个任意类型的参数例子:
TestController 下的 public修饰,返回类型为String ⽅法名为t1的⽆参⽅法
execution(public String com.example.demo.TestController.t1())
匹配 TestController 下的所有⽆参⽅法
execution(* com.example.demo.TestController.*())
匹配controller包下所有的类的所有⽅法
execution(* com.example.demo.controller.*.*(..))
3.5.2 @annotation
当我们要落实到不同类下个几个方法,用上面的execution就有点捉襟见肘。
我们就可以使用⾃定义注解的⽅式以及另⼀种切点表达式 @annotation 来描述这⼀类的切点。自定义注解:
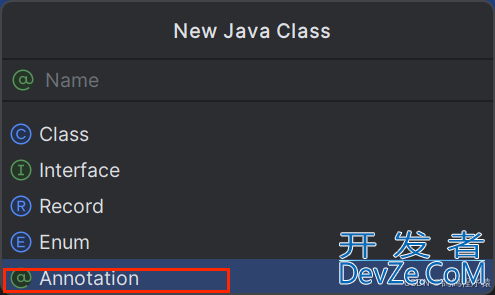
在自定义类的时候选择annotation:
然后就跟我们前面使用的注解一样包含,生命周期@Retention,作用范围@Target,交给Spring管理。
@Component
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAspect {
}
定义切面类:
- 使用@Aspect注解修饰,
- 交给Spring管理
- 在通知类型的注解中使用:@annotation(自定义注解路径) 作为参数。
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspectDemo {
@Around("@annotation( com.example.demoaop.MyAspect)")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
log.info("annotation 运行前");
pjp.proceed();
log.info("annotation 运行后");
}
}
通过上面的方法,使用了自定义注解修饰的方法,就可以添加切面类的通知。
@R编程equestMapping("/test")
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class Test {
@RequestMapping("/f1")
public String f1() {
log.info("f1");
return "s1";
}
@MyAspect
@RequestMapping("/f2")
public Integer f2() {
log.info("f2");
return 1;
}
@RequestMapping("/f3")
public Boolean f3() {
log.info("f3");
return false;
}
}
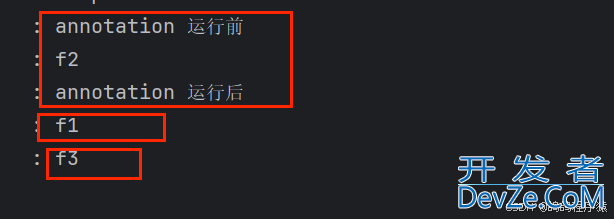
访问f2 f1 f3 的结果:
除了上面讲的基于注解的方式实现Spring AOP 还有远古的通过XML和代理的方式实现。参考Spring AOP其它实现方式
到此这篇关于Spring AOP的注解实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring AOP注解实现内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!

 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论