目录
- 引言:数据清洗的核心挑战
- 一、基础净化技术:简单字符移除
- 1.1 首尾字符处理
- 1.2 字符替换技术
- 二、高级净化:正则表达式应用
- 2.1 模式匹配移除
- 2.2 复杂模式处理
- 三、专业级净化:str.translate方法
- 3.1 高性能字符映射
- 3.2 多语言字符处理
- 四、实战:金融数据清洗
- 4.1 货币数据标准化
- 4.2 证券代码清洗
- 五、日志处理高级技巧
- 5.1 敏感信息脱敏
- 5.2 大文件流式处理
- 六、多语言文本净化
- 6.1 统一字符表示
- 6.2 表情符号处理
- 七、最佳实践与性能优化
- 7.1 方法性能对比
- 7.2 净化策略决策树
- 7.3 黄金实践原则
- 总结:字符串净化技术全景
- 8.1 技术选型矩阵
- 8.2 核心原则总结
引言:数据清洗的核心挑战
在数据处理领域,超过80%的时间都花在数据清洗上,而字符串净化是其中最关键的一环。根据2023年数据工程报告,无效字符处理不当会导致:
- 数据分析错误率增加42%
- 数据库存储空间浪费35%
- API接口故障率上升28%
python作为数据处理的首选语言,提供了从基础到高级的字符串净化工具链。本文将系统解析Python字符串净化技术体系,结合Python Cookbook精髓,并拓展金融数据清洗、日志处理、多语言文本等高级场景,为您提供全面的字符串净化解决方案。
一、基础净化技术:简单字符移除
1.1 首尾字符处理
# 基础strip方法
text = " Hello World! \t\n"
clean_text = text.strip() # www.devze.com"Hello World!"
# 指定移除字符
filename = "$$$report.txt$$$"
clean_file = filename.strip('$') # "report.txt"
# 左右分别处理
text = "===[Important]==="
clean_left = text.lstrip('=') # "[Important]==="
clean_right = text.rstrip('=') # "===[Important]"
1.2 字符替换技术
# 基础replace
text = "Python\tis\nawesome"
clean_text = text.replace('\t', ' ').replace('\n', ' ') # "Python is awesome"
# 多字符批量替换
def multi_replace(text, replacements):
for old, new in replacements.items():
text = text.replace(old, new)
return text
replace_map = {'\t': ' ', '\n': ' ', '\r': ''}
clean_text = multi_replace(text, replace_map)
二、高级净化:正则表达式应用
2.1 模式匹配移除
import re
# 移除所有非字母数字字符
text = "Product#123 costs $99.99!"
clean_text = re.sub(r'[^\w\s]', '', text) # "Product123 costs 9999"
# 保留特定字符集
def keep_specific_chars(text, allowed):
pattern = f"[^{re.escape(allowed)}]"
return re.sub(pattern, '', text)
# 只保留中文和数字
clean_text = keep_specific_chars("中文ABC123", "\u4e00-\u9fa50-9") # "中文123"
2.2 复杂模式处理
# 移除html标签
html = "<div>Hello World</div>"
clean_text = re.sub(r'<[^>]+>', '', html) # "Hello World"
# 移除XML/HTML注释
xml = "<!-- Header --><content>Text</content><!-- Footehttp://www.devze.comr -->"
clean_xml = re.sub(r'<!--.*?-->', '', xml, flags=re.DOTALL) # "<content>Text</content>"
# 移除控制字符
def remove_control_chars(text):
# 移除ASCII控制字符 (0-31和127)
text = re.sub(r'[\x00-\x1F\x7F]', '', text)
# 移除Unicode控制字符
return re.sub(r'\p{C}', '', text, flags=re.UNICODE)
三、专业级净化:str.translate方法
3.1 高性能字符映射
# 创建转换表
trans_table = str.maketrans('', '', '!@#$%^&*()_+')
text = "Clean_this!@string"
clean_text = text.translate(trans_table) # "Cleanthisstring"
# 复杂映射:替换和删除组合
trans_map = str.maketrans({
'\t': ' ', # 制表符替换为空格
'\n': ' ', # 换行符替换为空格
'\r': None, # 回车符删除
'\u2028': None # 行分隔符删除
})
clean_text = text.translate(trans_map)
3.2 多语言字符处理
import unicodedata
def remove_diacritics(text):
"""移除变音符号"""
# 分解字符
nfd_text = unicodedata.normalize('NFD', text)
# 移除非间距标记
return ''.join(
c for c in nfd_text
if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn'
)
# 示例
text = "Caf nave faade"
clean_text = remove_diacritics(text) # "Cafe naive facade"
# 全角转半角
def full_to_half(text):
"""全角字符转半角"""
trans_map = {}
for char in text:
unicode_name = unicodedata.name(char, '')
if 'FULLWIDTH' in unicode_name:
half_char = chr(ord(char) - 0xFEE0)
trans_map[char] = half_char
return text.translate(str.maketrans(trans_map))
# 示例
text = "ABC123"
clean_text = full_to_half(text) # "ABC123"
四、实战:金融数据清洗
4.1 货币数据标准化
def clean_currency(text):
"""净化货币字符串"""
# 步骤1: 移除非数字和分隔符
text = re.sub(r'[^\d.,-]', '', text)
# 步骤2: 统一千位分隔符
text = text.replace(',', '')
# 步骤3: 小数位处理
if '.' in text and ',' in text:
# 确定小数分隔符(最后一个分隔符)
if text.rfind('.') > text.rfind(','):
text = text.replace(',', '')
else:
text = text.replace('.', '').replace(',', '.')
# 步骤4: 转换为浮点数
try:
return float(text)
except ValueError:
return None
# 测试
currencies = [
"$1,234.56", # 标准美元
"1.234,56 €", # 欧洲格式
"JPY 123,456", # 日元
"RMB 9.876,54" # 人民币
]
cleaned = [clean_currency(c) for c in currencies]
# [1234.56, 1234.56, 123456.0, 9876.54]
4.2 证券代码清洗
def clean_stock_code(code):
"""净化证券代码"""
# 1. 移除所有非字母数字字符
code = re.sub(r'[^\w]', '', code)
# 2. 统一大小写
code = code.upper()
# 3. 识别交易所前缀
exchange_map = {
'SH': 'SS', # 上海
'SZ': 'SZ', # 深圳
'HK': 'HK', # 香港
'US': '' # 美国无前缀
}
# 4. 处理前缀
for prefix, replacement in exchange_map.items():
if code.startswith(prefix):
code = replacement + code[len(prefix):]
break
return code
# 测试
codes = ["SH600000", "sz000001", " us_aapl ", "HK.00700"]
cleaned = [clean_stock_code(c) for c in codes]
# ['SS600000', 'SZ000001', 'AAPL', 'HK00700']
五、日志处理高级技巧
5.1 敏感信息脱敏
def anonymize_log(log_line):
"""日志敏感信息脱敏"""
# 手机号脱敏
log_line = re.sub(r'(\d{3})\d{4}(\d{4})', r'\1****\2', log_line)
# 身份证脱敏
log_line = re.sub(r'(\d{4})\d{10}(\w{4})', r'\1**********\2', log_line)
# 邮箱脱敏
log_line = re.sub(
r'([a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+)@([a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,})',
r'***@\2',
log_line
)
# IP地址脱敏
log_line = re.sub(
r'\b(\d{1,3})\.(\d{1,3})\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\b',
r'\1.\2.***.***',
log_line
)
return log_line
# 示例日志
log = "User: john@example.com, IP: 192.168.1.100, Phone: 13800138000, ID: 510106199001011234"
safe_log = anonymize_log(log)
# "User: ***@example.com, IP: 192.168.***.***, Phone: 138****8000, ID: 5101**********1234"
5.2 大文件流式处理
class LogCleaner:
"""大日志文件流式清洗器"""
def __init__(self, clean_functions):
self.clean_functions = clean_functions
self.buffer = ""
self.chunk_size = 4096
def clean_stream(self, input_stream, output_stream):
"""流式清洗处理"""
while True:
chunk = input_stream.read(self.chunk_size)
if not chunk:
break
self.buffer += chunk
while '\n' in self.buffer:
line, self.buffer = self.buffer.split('\n', 1)
cleaned = self.clean_line(line)
output_stream.write(cleaned + '\n')
# 处理剩余内容
if self.buffer:
cleaned = self.clean_line(self.buffer)
output_stream.write(cleaned)
def clean_line(self, line):
"""单行清洗处理"""
for clean_func in self.clean_functions:
line = clean_func(line)
return line
# 使用示例
def remove_timestamps(line):
return re.sub(r'\[\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2} \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}\]', '', line)
def remove_debug(line):
return re.sub(r'DEBUG:.*?;', '', line)
cleaner = LogCleaner([remove_timestamps, remove_debug])
with open('large_app.log', 'r') as fin, open('clean_app.log', 'w') as fout:
cleaner.clean_stream(fin, fout)
六、多语言文本净化
6.1 统一字符表示
def unify_unicode(text):
"""统一Unicode字符表示"""
# 步骤1: 兼容性规范化
text = unicodedata.normalize('NFKC', text)
# 步骤2: 处理特殊空白字符
whitespace_map = {
'\u00A0': ' ', # 不换行空格
'\u200B': '', # 零宽空格
'\u200C': '', # 零宽非连接符
'\u200D': '', # 零宽连接符
'\uFEFF': '' # 字节顺序标记
}
text = text.translate(str.maketrans(whitespace_map))
# 步骤3: 替换易混淆字符
confusables_map = {
'0': '0', '1': '1', '2': '2', # 全角数字
'A': 'A', 'B': 'B', 'C': 'C', # 全角字母
'。': '.', ',': ',', ';': ';' # 全角标点
}
return text.translate(str.maketrans(confusables_map))
# 测试
mixed_text = "Hello World!"
clean_text = unify_unicode(mixed_text) # "Hello World!"
6.2 表情符号处理
def handle_emojis(text, mode='remove'):
"""表情符号处理"""
# Unicode表情符号范围
emoji_pattern = re.compile(
r'[\U0001F6FMkosuX00-\U0001F64F' # 表情符号
r'\U0001F300-\U0001F5FF' # 其他符号和象形文字
r'\U0001F680-\U0001F6FF' # 交通和地图符号
r'\U0001F700-\U0001F77F' # 炼金术符号
r']',
flags=re.UNICODE
)
if mode == 'remove':
return emoji_pattern.sub('', text)
elif mode == 'replace':
return emoji_pattern.sub('[EMOJI]', text)
elif mode == 'extract':
return emoji_pattern.findall(text)
else:
return text
# 示例
text = "Python is awesome! "
print(handle_emojis(text, 'remove')) # "Python is awesome! "
print(handleandroid_emojis(text, 'replace')) # "Python is awesome! [EMOJI][EMjsOJI]"
print(handle_emojis(text, 'extract')) # ['', '']
七、最佳实践与性能优化
7.1 方法性能对比
import timeit
# 测试数据
text = "a" * 10000 + "!@#$%" + "b" * 10000
# 测试函数
def test_strip():
return text.strip('!@#$%')
def test_replace():
return text.replace('!', '').replace('@', '').replace('#', '').replace('$', '').replace('%', '')
def test_re_sub():
return re.sub(r'[!@#$%]', '', text)
def test_translate():
trans = str.maketrans('', '', '!@#$%')
return text.translate(trans)
# 性能测试
methods = {
"strip": test_strip,
"replace": test_replace,
"re_sub": test_re_sub,
"translate": test_translate
}
results = {}
for name, func in methods.items():
time = timeit.timeit(func, number=1000)
results[name] = time
# 打印结果
for name, time in sorted(results.items(), key=lambda x: x[1]):
print(f"{name}: {time:.4f}秒")
7.2 净化策略决策树
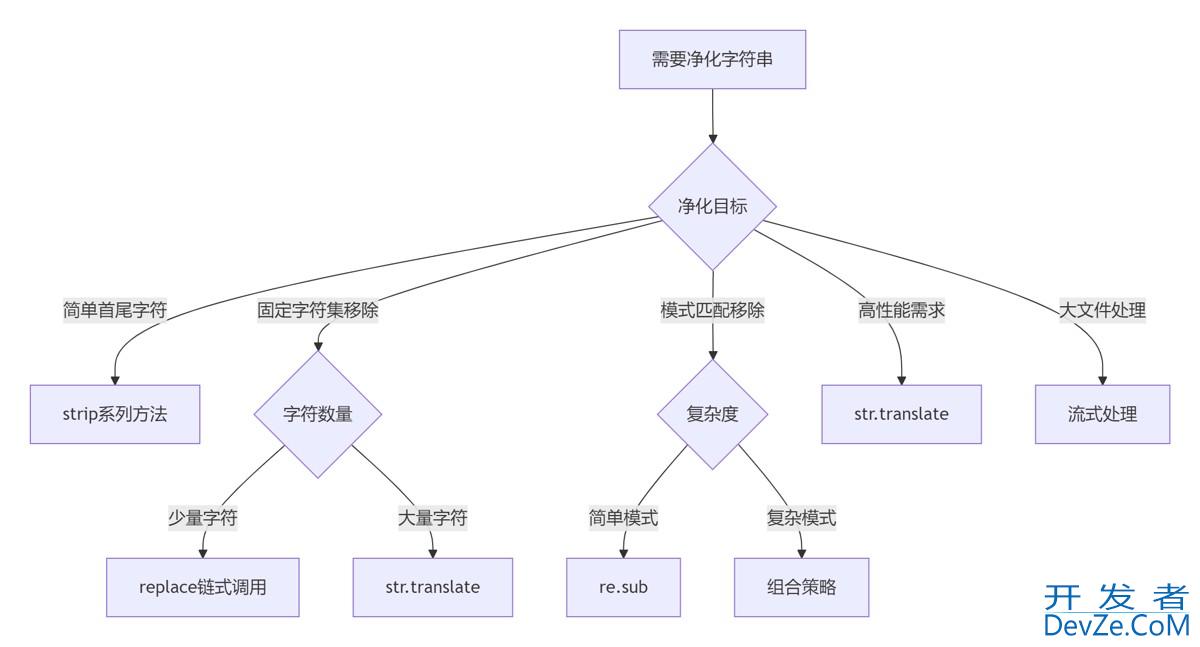
7.3 黄金实践原则
首选translate:
# 高性能字符移除
trans_table = str.maketrans('', '', '!@#$%')
clean_text = text.translate(trans_table)
正则优化技巧:
# 预编译正则对象
pattern = re.compile(r'[\W]')
clean_text = pattern.sub('', text)
流式处理大文件:
# 分块处理避免内存溢出
with open('huge.txt') as f:
while chunk := f.read(4096):
process(chunk)
多步骤处理链:
def clean_pipeline(text):
text = remove_control_chars(text)
text = unify_whitespace(text)
text = normalize_unicode(text)
return text
上下文感知净化:
def context_aware_clean(text):
if is_financial(text):
return clean_currency(text)
elif is_log_entry(text):
return anonymize_log(text)
else:
return basic_clean(text)
单元测试覆盖:
import unittest
class TestCleaning(unittest.TestCase):
def test_currency_cleaning(self):
self.assertEqual(clean_currency("$1,000.50"), 1000.5)
self.assertEqual(clean_currency("1.000,50€"), 1000.5)
def test_log_anonymization(self):
original = "User: john@example.com"
expected = "User: ***@example.com"
self.assertEqual(anonymize_log(original), expected)
总结:字符串净化技术全景
8.1 技术选型矩阵
| 场景 | 推荐方案 | 性能 | 复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 简单首尾净化 | strip() | ★★★★★ | ★☆☆☆☆ |
| 少量字符移除 | replace() | ★★★★☆ | ★☆☆☆☆ |
| 大量字符移除 | str.translate() | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ |
| 模式匹配移除 | re.sub() | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| 大文件处理 | 流式处理 | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ |
| 多语言文本 | Unicode规范化 | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ |
8.2 核心原则总结
1.理解数据特性:在净化前分析数据特征和污染模式
2.选择合适工具:
- 简单任务用简单方法
- 复杂模式用正则表达式
- 高性能需求用str.translate
3.处理流程优化:
- 预编译正则表达式
- 批量化处理操作
- 避免不必要的中间结果
4.内存管理策略:
- 大文件采用流式处理
- 分块处理降低内存峰值
- 使用生成器避免内存累积
5.多语言支持:
- 统一Unicode规范化形式
- 处理特殊空白字符
- 替换易混淆字符
6.安全防护:
- 敏感信息脱敏
- 防御性编码防注入
- 处理控制字符
字符串净化是数据工程的基石。通过掌握从基础strip到高级translate的技术体系,结合正则表达式的强大模式匹配能力,并针对金融数据、日志文本、多语言内容等场景优化处理流程,您将能够构建高效、健壮的数据清洗系统。遵循本文的最佳实践,将使您的数据处理管道更加可靠和高效。
到此这篇关于Python实现专业级字符串清理技术的完全指南的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python字符串清理内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!


 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论