目录
- 一、为什么需要动态刷新配置?
- 二、@RefreshScope核心原理
- 1. 工作原理图解
- 2. 关键技术解析
- 三、完整实现步骤
- 步骤1:添加必要依赖
- 步骤2:启用刷新机制
- 步骤3:配置application.yml
- 步骤4:创建动态配置Bean
- 步骤5:创建测试控制器
- 步骤6:触发配置刷新
- 四、深入理解@RefreshScope
- 1. 作用域代理原理
- 2. 刷新范围控制技巧
- 五、生产环境最佳实践
- 1. 安全加固配置
- 2. 自动刷新方案
- 六、常见问题排查
- 问题1:刷新后配置未生效
- 问题2:多实例刷新不同步
- 问题3:配置更新导致内存泄漏
- 七、扩展应用场景
- 结语:拥抱动态配置新时代
无需重启服务,实时更新配置! 本文将深入探索Spring Boot中@RefreshScope的神奇力量,让你的应用配置在运行时动态刷新,彻底告别服务重启的烦恼。
一、为什么需要动态刷新配置?
在传统Java应用中,修改配置文件后必须重启服务才能生效,这会导致:
- 服务中断:重启期间服务不可用
- 状态丢失:内存中的临时数据被清空
- 运维复杂:需要复杂的发布流程
Spring Boot的@RefreshScope完美解决了这些问题,实现配置热更新,让应用像乐高积木一样灵活重组!
二、@RefreshScope核心原理
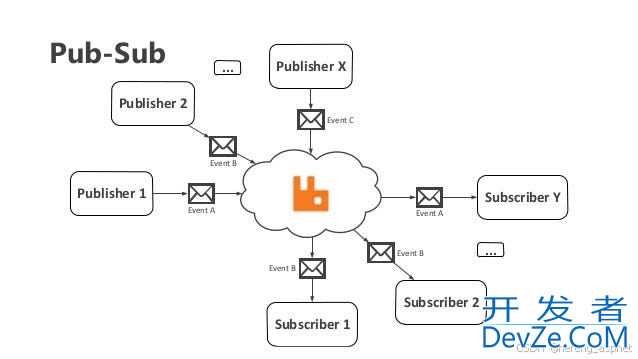
1. 工作原理图解
graph TD
A[修改配置文件] --> B[发送POST刷新请求]
B --> C[/actuator/refresh 端点]
C --> D[RefreshScope 刷新机制]
D --> E[销毁旧Bean并创建新Bean]
E --> F[新配置立即生效]
2. 关键技术解析
- 作用域代理:为Bean创建动态代理,拦截方法调用
- 配置绑定:当配置更新时,重新绑定
@Value注解的值 - Bean生命周期管理:销毁并重新初始化被
@RefreshScope标记的Bean
三、完整实现步骤
步骤1:添加必要依赖
<!-- pom.XML -->
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot基础依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 配置刷新核心 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 配置中心支持 -->
<dependephpncy>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud&编程客栈lt;/groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.1.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
步骤2:启用刷新机制
// 主应用类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableRefreshScope // 关键注解:开启配置刷新能力
public class DynamicConfigApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DynamicConfigApp.class, args);
}
}
步骤3:配置application.yml
# 应用基础配置
app:
feature:
enabled: true
timeout: 5000
retry-count: 3
welcome-msg: "Hello, Dynamic Config!"
# 暴露刷新端点(关键!)
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: refresh,health,info
步骤4:创建动态配置Bean
@Service
@RefreshScope // 标记此Bean支持动态刷新
public class FeatureService {
// 注入可刷新的配置项
@Value("${app.feature.enabled}")
private boolean featureEnabled;
@Value("${app.feature.timeout}")
private int timeout;
@Value("${app.feature.retry-count}")
private int retryCount;
@Value("${app.feature.welcome-msg}")
private String welcomeMessage;
public String getFeatureConfig() {
return String.format("""
Feature Enabled: %s
Timeout: %d ms
Retry Count:http://www.devze.com %d
Message: %s
""", featureEnabled, timeout, retryCount, welcomeMessage);
}
}
步骤5:创建测试控制器
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/config")
public class ConfigController {
private final FeatureService featureService;
// 构造函数注入
public ConfigController(FeatureService featureService) {
this.featureService = featureService;
}
@GetMapping
public String getConfig() {
return featureService.getFeatureConfig();
}
}
步骤6:触发配置刷新
修改application.yml后,发送刷新请求:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/actuator/refresh
响应示例(返回被修改的配置项):
["app.feature.timeout", "app.feature.welcome-msg"]
四、深入理解@RefreshScope
1. 作用域代理原理
// 伪代码:Spring如何实现动态刷新
public class RefreshScopeProxy implements ApplicationContextAware {
private Object targetBean;
@Override
public Object invoke(Method method) {
if (conwww.devze.comfigChanged) {
// 1. 销毁旧Bean
context.destroyBean(targetBean);
// 2. 重新创建Bean
targetBean = context.getBean(beanName);
}
return method.invoke(targetBean, args);
}
}
2. 刷新范围控制技巧
场景1:只刷新特定Bean的部分属性
@Component
@RefreshScope
public class PaymentService {
// 只有带@Value的属性会刷新
@Value("${payment.timeout}")
private int timeout;
// 不会被刷新的属性
private final String apiVersion = "v1.0";
}
场景2:组合配置类刷新
@Configuration
@RefreshScope // 整个配置类可刷新
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
@RefreshScope
public FeatureService featureService() {
return new FeatureService();
}
@Value("${app.theme}")
private String theme;
}
五、生产环境最佳实践
1. 安全加固配置
management:
endpoint:
refresh:
enabled: true
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: refresh
base-path: /internal # 修改默认路径
path-mapping:
refresh: secure-refresh # 端点重命名
# 添加安全认证
spring:
security:
user:
name: admin
password: $2a$10$NVM0n8ElaRgg7zWO1CxUdei7vWoQP91oGycgVNCY8GQEx.TGx.AaC
2. 自动刷新方案
方案1:Git Webhook自动刷新
代码仓库Spring Boot应用CI服务器配置文件变更推送调用/actuator/refresh刷新配置代码仓库Spring Boot应用CI服务器方案2:配置中心联动(Nacos示例)
// bootstrap.yml
spring:
cloud:
nacos:
config:
server-addr: localhost:8848
auto-refresh: true # 开启自动刷新
六、常见问题排查
问题1:刷新后配置未生效
解决方案:
- 检查是否添加
@RefreshScope - 确认刷新端点返回了修改的配置项
- 查看日志:
logging.level.org.springframework.cloud=DEBUG
问题2:多实例刷新不同步
解决方案:
# 使用Spring Cloud Bus同步刷新 curl -X POST http://host:port/actuator/bus-refresh
问题3:配置更新导致内存泄漏
预防措施:
@PreDestroy
public void cleanUp() {
VoiuaLE// 清理资源
}
七、扩展应用场景
动态功能开关:实时开启/关闭功能模块
# 修改后立即生效 feature.new-checkout.enabled=true
运行时日志级别调整
@RefreshScope public class LogConfig { @Value("${logging.level.root}") private String logLevel; // 动态应用新日志级别 }数据库连接池调优
# 动态修改连接池配置 spring.datasource.hikari.maximum-pool-size=20
结语:拥抱动态配置新时代
通过@RefreshScope,我们实现了:
最佳实践建议:
- 敏感配置(如密码)避免使用动态刷新
- 配合配置中心(Nacos/Config Server)使用
- 生产环境务必保护刷新端点
到此这篇关于SpringBoot结合@RefreshScope实现动态刷新配置的示例的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot @RefreshScope动态刷新内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!


 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论