目录
- 什么是场景启动器?
- SpringBoot父项目spring-boot-starter-parent主要作用?
- maven从0开始搭建SpringBoot项目
- 1. pom文件导入SpringBoot父依赖
- 2. 编写SpringBootApplication启动类
- 3. 创建控制器,测试SpringBoot项目能否正常启动
- SpringBoot整合Spring MVC
- 什么是 WebMvcConfigurer?
- SpringBoot整合拦截器Interceptor
- 整合步骤
- SpringBoot外部配置
- 功能配置
- SpringBoot:配置端口和项目根路径
- SpringBoot:多环境Profile配置和切换
- 自定义配置
- spring注解读取配置文件
- SpringBoot注解批量读取配置文件
- SpringBoot测试环境
- 方式一:测试类在启动类所在包
- 方式二:测试类通过注解指定启动类
- 其他扩展
- 项目父依赖spring-boot-starter-parent必须要引用吗?不引用可以使用SpringBoot项目吗?
- 1. 选择:spring-boot-starter-parent- 省心省力
- 2. 选择:依赖管理导入 - 自由设计,个性定制
- 认识SpringBootApplication启动器类
- @SpringBootApplication启动器注解说明
什么是场景启动器?
定义:
场景启动器(Starters) 是 Spring Boot 的核心特性之一,是一组预定义的依赖描述符(Maven工程),可以简化Maven配置。它们通常提供了一种“一站式”服务,预先添加所有必要的依赖来使用某个特定的功能,可以轻松地将相关技术栈集成到项目中。- 例如,如果你想要使用
Spring和JPA进行数据库访问,你只需要添加spring-boot-starter-data-jpa依赖即可,它会自动引入所有相关的依赖。
核心理念:
- 开箱即用:添加一个 starter 即可获得完整的技术栈支持
- 依赖管理:自动解决版本兼容性问题
- 自动配置:基于
classpath自动配置相关组件
优势: 简化整合、简化开发、简化配置
简化整合(项目依赖):
- springboot提供了一种场景启动器机制。
- 场景启动器就是人为创建的maven整合工程。
- 场景启动器中包含某个场景(方向)所有的依赖和配置类。
- 场景启动器可以在普通maven工程使用,也可以在springboot工程使用
- springboot工程才能发挥最大的功能:批量依赖导入、配置类自动加载
- 官方场景启动器命名:
spring-boot-starter-xxx - 非官方场景启动器命名:xxx-
spring-boot-starter
简化开发(核心组件):
- 无需我们写任何的配置类和配置文件(IOC)
- springboot在场景启动器中已经提供所有的配置类
- springboot框架自动配置功能(原理)
- springboot自动配置原理会按需加载配置类,按需将组件加入到核心容器
- 我们只需要专注业务逻辑编写即可。
简化配置(配置文件):
- 固定配置文件的名称和格式。
application.properties、.yaml - 固定了部分功能的key(直接设置即可)
- 固定的key大部分都有默认值(约定大于配置)
- 不仅可以使用
@Value注解单个读取,还可以使用@ConfigurationProperties注解批量读取
下面列出一些常见的Spring Boot场景启动器:
spring-boot-starter: 核心启动器,包括自动配置支持、日志和YAML。spring-boot-starter-web: 用于构建Web应用程序,包括RESTful应用程序,使用Spring MVC。默认使用Tomcat作为编程客栈内嵌容器。spring-boot-starter-data-Redis: 使用Redis和Spring Data Redis。spring-boot-starter-security: 使用Spring Security进行身份验证和授权。spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf: 使用Thymeleaf视图构建Web应用程序。spring-boot-starter-test: 用于测试Spring Boot应用程序,包括JUnit、Hamcrest和Mockito。spring-boot-starter-actuator: 添加生产就绪功能,如监控和管理应用程序。spring-boot-starter-undertow: 使用Undertow作为内嵌容器(替代Tomcat和Jetty)。spring-boot-starter-log4j2: 使用Log4j2进行日志记录。
除了官方提供的启动器,还有很多第三方启动器,例如:
myBATis-spring-boot-starter: 用于集成MyBatis。druid-spring-boot-starter: 用于集成阿里巴巴的Druid数据源。
官方和第三方的场景启动器区别?
- 官方启动器的前缀为:
spring-boot-starter,后跟项目名称。 - 第三方启动器的前缀为:项目名称-
spring-boot-starter。 mybatis是第三方场景启动器,它与web格式的区别在于它的名称在前面。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>
SpringBoot父项目spring-boot-starter-parent主要作用?
我们创建SpringBoot项目时,通常会导入spring-boot-starter-parent场景启动器作为父项目,帮助我们管理并简化依赖的版本号。我们在确定要导入的spring-boot-starter-parent版本后,后续的导入的依赖就不需要写入版本信息了,spring-boot-starter-parent启动器会帮我们选择合适的场景启动器的版本好信息。
spring-boot-starter-parent底层是如何帮助我们实现的场景启动器版本管理呢?
- 首先
spring-boot-starter-parent场景启动器继承自spring-boot-dependencies,而spring-boot-dependencies的内部通过使用dependencyManagement来管理这些依赖的版本号。 - 也就是说实际完成版本号管理的是
spring-boot-dependencies工程。 - 而
spring-boot-starter-parent的管理版本号的功能继承自spring-boot-dependencies。 - 而
spring-boot-starter-parent主要功能在于管理一些通用的构建配置,比如默认的编译器版本、资源过滤、插件配置等。
这样的设计是为了将依赖管理(dependency management)和插件配置等分开,使得项目结构更清晰。
在 Spring Boot 的源码中,spring-boot-starter-parent 的 pom.XML 中确实指定了其父项目为 spring-boot-dependencies。
这样的层次结构有以下好处:
spring-boot-dependencies主要定义了依赖管理(dependencyManagement)和插件管理(pluginManagement),即所有依赖的版本号 和插件的版本号。spring-boot-starter-parent则继承自spring-boot-dependencies,并添加了一些通用的构建配置,比如默认的编译器版本、资源过滤、插件配置等。- 当用户项目继承
spring-boot-starter-parent时,不仅获得了依赖版本管理,还获得了一些构建相关的默认配置。
所以,我们可以这样理解:
spring-boot-dependencies:定义了所有依赖的版本,即一个大的依赖管理矩阵。spring-boot-starter-parent:在依赖管理的基础上,增加了默认的构建配置(如 Maven 插件配置、资源过滤等)。
如果你查看 spring-boot-starter-parent 的 pom.xml,你会看到它并没有重复定义依赖版本,而是通过继承 spring-boot-dependencies 来获得所有版本管理。同时,它定义了一些其他元素,比如:
- 默认的 Java 版本
- 资源过滤(包括占位符解析)
- 插件配置(如 spring-boot-maven-plugin 的默认配置)
因此,当我们在项目中继承 spring-boot-starter-parent 时,我们实际上同时获得了依赖管理和构建配置两方面的便利。
如果你不能继承 spring-boot-starter-parent(比如已经有一个父项目),那么你可以通过引入 spring-boot-dependencies 的依赖管理来获得版本管理,但是构建配置就需要自己处理了。
总结:spring-boot-starter-parent 的父工程是 spring-boot-dependencies,前者继承了后者的依赖管理,并补充了构建配置。
这也就是为什么在Springboot工程中,很多依赖不需要写版本号信息的原因。
maven从0开始搭建SpringBoot项目
1. pom文件导入SpringBoot父依赖
- 导入父依赖。
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.5.7</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
spring-boot-starter-parent专业特性:
- 依赖管理(Dependency Management):统一管理所有Spring Boot相关依赖的版本
- 插件配置(Plugin Configuration):预配置Maven插件,如spring-boot-maven-plugin
- 资源过滤(Resource Filtering):自动处理配置文件中的占位符替换
- 属性配置(Property Configuration):预定义Java版本、编码等构建属性
spring-boot-starter-parent优势:
- ✅ 开箱即用:不用操心版本兼容
- ✅ 配置齐全:插件、编码、Java版本都配好了
- ✅ 社区标准:遵循Spring Boot官方最佳实践
- ✅ 减少错误:避免手动配置出错
导入场景启动器
<dependencies>
<!--spring mvc场景启动器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2. 编写SpringBootApplication启动类
我们通常将带有@SpringBootApplication注解的类称为启动类(或主类),它是Spring Boot应用的入口点。
启动器类是一个配置类(Configuration Class),通过组合注解和自动配置机制,引导 Spring 容器的启动过程,实现零配置或最小配置的应用启动。
- 使用
SpringBoot注解@SpringBootApplication修饰类文件。 - 在入口函数
main()方法处,它会创建一个IOC容器。
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 启动tomcat和ioc容器
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
}
}
3. 创建控制器,测试SpringBoot项目能否正常启动
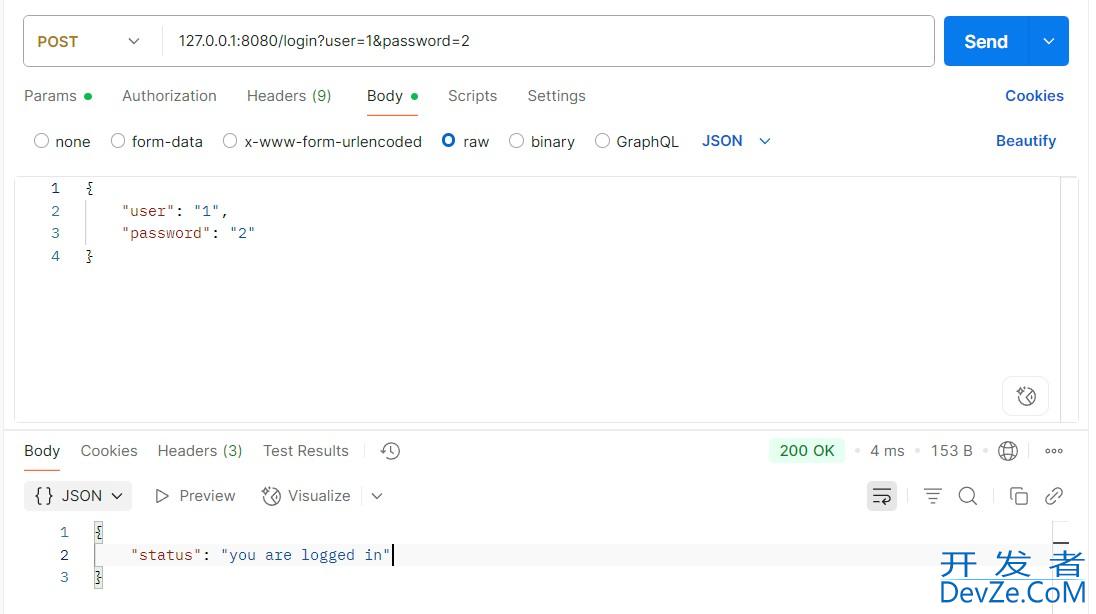
- 访问链接:localhost:8080/user/info,测试项目是否启动成功。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("info")
public String info(){
return "hello";
}
}
SpringBoot整合Spring MVC
Spring Boot 整合 Spring MVC 非常简便,因为 Spring Boot 已经为 Spring MVC 提供了自动配置。
- 我们只需要导入
spring-boot-starter-web场景启动器即可。
- 创建SpringBoot项目,导入WEB场景启动器。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 编写控制器
Controller。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("info")
public String info(){
return "user";
}
@GetMapping("login")
public String login(){
return "login";
}
}
- 访问控制器地址
- http://localhost:8080/user/info
什么是 WebMvcConfigurer?
WebMvcConfigurer 是 Spring MVC 框架中的一个核心接口,它提供了回调方法,允许开发者在 Spring MVC 自动配置的基础上进行定制化扩展。
WebMvcConfigurer是 Spring MVC 中用于自定义配置的核心接口,它提供了一种方式来自定义 Spring MVC 的行为,而无需完全重写自动配置。- 在 Spring Boot 中,自动配置已经为我们配置好了 Spring MVC 的大部分默认行为,但如果你需要添加拦截器、格式化器、视图控制器等,就可以通过实现
WebMvcConfigurer接口来定制。 - 我们通常使用
WebMvcConfigurer来配置Spring MVC,它替代了传统的XML配置方式。在Spring Boot中,我们通过实现WebMvcConfigurer接口并重写所需的方法来定制MVC配置,比如拦截器、资源处理、跨域配置等。
主要意义:
- 提供集中化的配置点:
WebMvcConfigurer允许开发者在一个或多个配置类中集中管理MVC配置,这有助于保持配置的一致性和可维护性。而不是分散在多个地方(如XML配置、注解配置等)。 - 保持与Spring Boot的自动配置协同工作:通过实现
WebMvcConfigurer接口,我们可以自定义MVC配置,而不会完全覆盖Spring Boot的自动配置。这是因为Spring Boot的WebMvcAutoConfiguration类已经提供了默认的MVC配置,并且它使用WebMvcConfigurer来允许自定义。这种方式遵循了“约定优于配置”的原则,同时提供了灵活性。 - 支持多种自定义场景:
WebMvcConfigurer提供了多个方法,覆盖了MVC的各个方面,包括拦截器、资源处理、跨域、视图控制器、消息转换器等。这意味着开发者可以在不破坏原有框架结构的情况下,针对特定需求进行定制。 - 促进模块化配置:通过实现
WebMvcConfigurer,我们可以创建多个配置类,每个配置类负责一个特定的功能模块(例如,安全模块、API模块、视图模块等)。这种模块化的配置方式使得应用更容易扩展和维护。 - 便于测试和调试:由于配置是集中且明确的,因此可以更容易地编写测试来验证配置是否正确,并且在调试时可以快速定位问题。
- 适应现代Web开发需求:现代Web应用通常需要处理静态资源、跨域请求、异步处理、内容协商等。
WebMvcConfigurer提供了对应的方法来配置这些特性,使应用能够满足现代Web标准。
SpringBoot整合拦截器Interceptor
整合步骤
- 创建SpringBoot项目,选择导入
spring-boot-starter-web场景启动器。 - 编写控制器
UserController。 - 创建一个拦截器
UserInterceptor实现HandlerInterceptor接口。
public class UserInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("拦截器 = preHandle");
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("拦截器 = postHandle");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("拦截器 = afterCompletion");
}
}
- 自定义
Spring MVC配置类,实现WebMvcConfigurer接口。
WebMvcConfigurer是 Spring MVC 提供的一个接口,用于自定义 Spring MVC 的配置。在 Spring Boot 中,我们可以通过实现这个接口来覆盖默认的 MVC 配置,例如添加拦截器、格式化器、视图控制器等。
@Configuration
public class SpringMvcConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new UserInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/user/**")
.excludePathPatterns("/user/login");
}
}
- 访问
UserController控制器方法。
- http://localhost:8080/user/info
- 触发拦截器
拦截器 = preHandle 拦截器 = postHandle 拦截器 = afterCompletion
SpringBoot外部配置
Spring Boot的外部配置是指从应用代码包外部获取配置信息的机制。它允许开发者将配置信息(如数据库连接、服务器端口等)从代码中分离出来,使得应用能够在不修改源代码和重新弄编译的情况下适应不同的运行环境。
定义
外部配置:指不直接在应用代码中硬编码配置值,而是通过外部源(如配置文件、环境变量、命令行参数等)来提供配置信息,Spring Boot会按照预定的优先级顺序加载这些配置。含义
外部配置的含义在于实现配置与代码的分离,它是一个分层、有序的配置加载系统,它从多个预定义的位置读取配置信息,并按照优先级顺序进行合并,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置。使得应用具有更好的可移植性和可维护性。通过外部配置,我们可以轻松地为不同环境(开发、测试、生产)定义不同的配置,而无需修改代码。
优势
- 灵活性:应用可以根据部署环境动态改变配置,而无需重新编译代码。
- 安全性:敏感信息(如密码、密钥)可以不写在代码中,而是通过外部配置传入,减少泄露风险。
- 环境适配:通过Profile机制,可以轻松切换不同环境的配置。
- 运维友好:运维人员可以通过命令行参数或环境变量快速调整配置,无需理解代码结构。
- 云原生支持:在容器化部署(如docker)和云平台(如Kubernetes)中,外部配置是标准做法,可以方便地通过环境变量或配置映射来注入配置。
Spring Boot 的外部配置是一个开放体系:
- 有固定的:Spring Boot 核心框架提供的标准配置
- 有扩展的:各种 Starter 提供的领域特定配置(
Mybatis-spring-boot-starter) - 有自定义的:开发者根据业务需求定义的任意配置
外部配置源
Spring Boot 可以以下面这些方式加载外部配置,优先级从高到低(高优先级配置会覆盖低优先级配置):- 命令行参数:通过java -jar命令传递的参数,例如:
java -jar app.jar --server.port=8081 - Java系统属性:使用
System.getProperties()获取的属性 - 操作系统环境变量
- 从jar包外部的配置文件:例如,在jar包同一目录下的
application-{profile}.properties或application-{profile}.yml文件 - 从jar包内部的配置文件:打包在jar包内的
application-{profile}.properties或application-{profile}.yml文件 - 默认配置:通过
SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties设置的默认属性
此外,Spring Boot 还支持通过@PropertySource注解加载自定义的配置文件,但注意这个注解不会加载application.properties文件,而是加载指定的其他文件。
配置文件的加载位置
Spring Boot 会从以下位置加载application.properties或application.yml文件:
- 当前目录的
/config子目录 - 当前目录
- classpath下的
/config包 - classpath根目录
这些位置按优先级从高到低排列,高位置的配置会覆盖低位置的配置。
application.properties配置文件的优先级高于application.yml。
功能配置
SpringBoot:配置端口和项目根路径
server:
port: 8080
servlet:
context-path: /demo
SpringBoot:多环境Profile配置和切换
Spring Boot 多环境配置允许我们为不同的环境(如开发、测试、生产)定义不同的配置。
我们可以通过配置文件(如application-{profile}.properties或application-{profile}.yml)来指定不同环境的配置,然后通过激活不同的profile来切换环境。
除了主配置文件application.properties,还可以使用命名约定为application-{profile}.properties的配置文件。其中{profile}是激活的配置文件名称。例如,application-dev.properties用于开发环境,application-prod.properties用于生产环境。
可以通过多种方式设置激活的profile,例如在配置文件中设置spring.profiles.active=dev,或者通过命令行参数--spring.profiles.active=dev。
多环境配置的主要步骤:
- 创建多个配置文件,分别对应不同的环境,例如:
src/main/resources/ ├── application.yml # 主配置文件,公共配置 ├── application-dev.yml # 开发环境配置 ├── application-test.yml # 测试环境配置 ├── application-prod.yml # 生产环境配置 └── application-staging.yml # 预生产环境配置
- 在主配置文件
application.yml中指定当前激活的环境,或者通过其他方式(如命令行参数、环境变量)来设置激活的环境。
- 主环境配置:默认激活开发环境
# 默认激活开发环境
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
- 开发环境配置:
application-dev.yml
# 开发环境配置:8080端口
server:
port: 8080
servlet:
context-path: /
- 生产环境配置:
application-prod.yml
# 生产环境配置:80端口
server:
port: 80
servlet:
context-path: /
- 若同时激活dev和prod环境,则后激活的配置会覆盖前面具有相同的配置。
- 主配置文件依然可以声明key!不受环境影响,如果相同,被激活的覆盖主配置文件。
- 在主配置文件中激活,属于静态激活。
spring:
profiles:
active: dev,prod
- 运行项目包的时候动态激活。
java -jar -Dspring.profiles.active=dev XXXXX.jar
自定义配置
spring注解读取配置文件
注意事项:
- Spring框架 的
@PropertySource默认只支持.properties文件,不支持.yaml或.yml文件。 - 若一定要使用
@PropertySource来读取YAML,则需要我们去配置一个PropertySourceFactory工厂类,实现YAML解析。 - 推荐使用SpringBoot中支持
yaml文件解析的ConfigurationProperties()注解。
@Data
@Component
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:animal.properties")
public class Animal {
@Value("${animal.dog.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${animal.dog.age}")
private Integer age;
@Value("${animal.dog.color}")
private String color;
@Value("${animal.dog.type}")
private String type;
}
- animal.properties配置文件:
animal.dog.name=small yellow animal.dog.age=18 animal.dog.color=black animal.dog.type=中华田园犬
SpringBoot注解批量读取配置文件
Spring Boot 允许将配置文件中的属性绑定到Java对象上,通常使用@ConfigurationProperties注解。
@ConfigurationProperties批量的配置参数读取:
- 最后一层和属性名相同,则自动映射。
- 配置文件中的key与对象属性要一一对应。
- 类上的配置注解:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "animal.dog")前缀要精确 - 属性和Key多写或者少写都没有关系,没有则被赋值为null。
application.yaml配置文件:
animal:
dog:
name: 狗
age: 18
color: 黑
type: 土狗
配置类:
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "animal.dog")
public class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String color;
private String type;
}
- 该代码会报错,因为缺少注册机制,
Spring找不到它
解决方案
方案1:使用 @EnableConfigurationProperties(推荐)
- 在主应用类或配置类上添加
@EnableConfigurationProperties:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties(value = {Dog.class}) // 明确注册 Dog 类
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
方案2:添加 @Component 注解
- 在
Dog类上添加@Component注解,让 Spring 自动扫描:
@Data
@Component // 添加组件注解
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "animal.dog")
public class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String color;
private String type;
}
方案3:使用 @ConfigurationPropertiesScan
在主应用类上添加 @ConfigurationPropertiesScan:
@SpringBootApplication
@ConfigurationPropertiesScan // 扫描所有 @ConfigurationProperties 类
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
// 或者指定扫描包
@SpringBootApplication
@ConfigurationPropertiesScan("com.example.config") // 指定包路径
public class Application {
// ...
}
方案4:在配置类中注册
- 创建一个配置类来注册配置属性:
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
@ConfphpigurationProperties(prefix = "animal.dog")
public Dog dog() {
return new Dog();
}
}
SpringBoot测试环境
SpringBoot的测试注解@SpringBootTest,会自动读取启动类。
- 测试类应该在启动类所在的包或者子包。
- 测试类不在启动类相同包或子包。
- 自己通过注解指定启动类!
@SpringBootTest(classes = XXXXApplication.class)
导入test场景启动器:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
方式一:测试类在启动类所在包
- 项目启动器类包路径:
src/main/java/com/animal/AnimalApplication.java - 测试类包路径:
src/test/java/com/animal/AnimalApplicationTests.java - 测试类与启动器类相同路径:
/java/com/animal/
package com.animal;
@SpringBootTest
class AnimalApplicationTests {
@Autowired
Animal animal;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println("animal = " + animal);
}
}
方式二:测试类通过注解指定启动类
- 项目启动器类包路径:
src/main/java/com/animal/AnimalApplication.java - 测试类包路径:
src/test/java/TestDemo.java - 测试类不在启动器类所在包或子包下。
- 通过注解指定启动器类,来启动测试环境。
@SpringBootTest(classes = AnimalApplication.class)
public class TestDemo {
@Autowired
Animal animal;
@Test
void test(){
System.out.println("animal = " + animal);
}
}
其他扩展
项目父依赖spring-boot-starter-parent必须要引用吗?不引用可以使用SpringBoot项目吗?
直接答案:不是必须的!
专业定义:spring-boot-starter-parent是一个Maven父POM(Project Object Model),它提供了Spring Boot项目的默认配置、依赖管理和插件配置。使用它是可http://www.devze.com选的,但强烈推荐。
Spring Boot 给了我们选择的自由。你可以:
1. 选择:spring-boot-starter-parent- 省心省力
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6</version>
</parent>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.cat.ssm</groupId>
<artifactId>cat-ssm</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
spring-boot-starter-parent专业特性:
- 依赖管理(Dependency Management):统一管理所有Spring Boot相关依赖的版本
- 插件配置(Plugin Configuration):预配置Maven插件,如spring-boot-maven-plugin
- 资源过滤(Resource Filtering):自动处理配置文件中的占位符替换
- 属性配置(Property Configuration):预定义Java版本、编码等构建属性
spring-boot-starter-parent优势:
- ✅ 开箱即用:不用操心版本兼容
- ✅ 配置齐全:插件、编码、Java版本都配好了
- ✅ 社区标准:遵循Spring Boot官方最佳实践
- ✅ 减少错误:避免手动配置出错
2. 选择:依赖管理导入 - 自由设计,个性定制
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring.boot.dependencies}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
- 父项目POM文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.sb.ssm</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-framework</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<spring.boot.dependencies>3.5.6</spring.boot.dependencies>
</properties>
<!--依赖管理-->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring.boot.dependencies}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.boot.dependencies}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<!--子项目-->
<modules>
<module>cat-ssm</module>
</modules>
<!-- 构建配置 -->
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- 必须手动配置所有插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
- 子项目POM文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.cat.ssm</groupId>
<artifapythonctId>cat-ssm</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>com.sb.ssm</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-framework</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
专业特性:
- BOM导入(Bill of Materials):通过
spring-boot-dependencies导入依赖版本管理 - 插件管理(Plugin Management):手动配置所有需要的Maven插件
- 自定义属性:完全控制构建环境和配置参数
dependencies的优势:
- ✅ 完全控制:自己决定所有配置
- ✅ 已有项目集成:已有父项目的可以无缝接入
- ✅ 企业规范:符合公司内部的Maven规范
- ✅ 灵活定制:可以混合其他技术栈
对于大多数 Spring Boot 项目,继承 spring-boot-starter-parent 是最简单、最安全的选择。
- 只有在有特殊需求或企业规范约束时,才考虑使用依赖管理导入的方式。
认识SpringBootApplication启动器类
在 @SpringBootApplication 注解中,这三个注解的组合使得 Spring Boot 应用能够:
- 通过
@SpringBootConfiguration标记主配置类,定义 bean。标记类为配置类,是@Configuration的特殊形式。 - 通过
@ComponentScan扫描组件,注册 bean。 - 通过
@EnableAutoConfiguration根据条件自动配置 bean。启用自动配置,根据classpath和已有配置自动配置 Spring 应用。
它们的执行顺序大致为:
- 首先,
@ComponentScan扫描并注册当前包及其子包下的组件。 - 然后,
@EnableAutoConfiguration根据条件自动配置其他 bean。
这种协同工作使得 Spring Boot 应用能够快速启动并运行,同时提供了极大的灵活性。
@SpringBootApplication启动器注解说明
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
}
@SpringBootConfiguration注解
详细解释:
@SpringBootConfiguration 是一个类级别的注解,它表明该类是一个配置类,并且是 Spring Boot 应用的配置类。
- 实际上,它是对
@Configuration注解的封装,两者在功能上是一样的。 - 但是,
@SpringBootConfiguration被设计为 Spring Boot 应用的主配置类,通常与@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan结合使用,形成@SpringBootApplication注解。
关键点:
- 它是一个特化的
@Configuration,用于 Spring Boot 应用。 - 它允许 Spring 容器通过调用同一配置类中的
@Bean方法来管理 bean 的依赖关系,因为默认情况下(proxyBeanMethods = true)会使用 CGLIB 代理来拦截对@Bean方法的调用,确保返回的是 Spring 容器中管理的单例 bean。 - 在大多数情况下,一个 Spring Boot 应用只有一个类被标注为
@SpringBootConfiguration,通常就是主启动类。
示例代码:
@SpringBootConfiguration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public MyService myService() {
return new MyServiceImpl();
}
@Bean
public MyRepository myRepository() {
return new MyRepositoryImpl();
}
}
@EnableAutoConfiguration
详细解释:
@EnableAutoConfiguration 是 Spring Boot 自动配置的核心注解。它通过 @Import 导入了 AutoConfigurationImportSelector,这个类会利用 Spring 的 SpringFactoriesLoader 机制从 classpath 下的 META-INF/spring.factories 文件中读取所有配置的自动配置类,然后根据条件注解(如 @ConditionalOnClass、@ConditionalOnBean 等)来决定是否启用这些自动配置类。
关键点:
- 自动配置类通常是一个
@Configuration类,但是它们只有在满足特定条件时才会被加载。 - 自动配置的顺序可以通过
@AutoConfigureOrder、@AutoConfigureBefore、@AutoConfigureAfter来调整。 - 我们可以通过
exclude或excludeName属性来排除不需要的自动配置类,也可以通过配置属性spring.autoconfigure.exclude来排除。
自动配置过程:
- 收集自动配置类:
AutoConfigurationImportSelector使用SpringFactoriesLoader从META-INF/spring.factories中加载EnableAutoConfiguration对应的配置类列表。 - 过滤自动配置类:通过条件注解(如
@ConditionalOnClass、@ConditionalOnBean等)过滤掉不满足条件的配置类。 - 应用自动配置:将过滤后的自动配置类加载到 Spring 容器中。
示例说明
假设我们有一个自动配置类用于配置数据源:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(DataSource.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.datasource.url")
//自动配置排序
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public class DataSourceAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public DataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
return properties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().build();
}
}
这个自动配置类只有在 classpath 下存在 D编程ataSource 类并且配置了 spring.datasource.url 属性时才会生效,而且只有在容器中没有 DataSource bean 时才会创建。
@ComponentScan注解
详细解释:
@ComponentScan 注解用于告诉 Spring 扫描指定包(及其子包)下的组件,包括 @Component、@Service、@Repository、@Controller 等注解标记的类,并将它们注册为 Spring bean。如果没有指定包,则默认扫描注解所在类的包及其子包。
关键点:
- 通过
basePackages或basePackageClasses属性指定要扫描的包。 - 可以使用
includeFilters和excludeFilters进行更细粒度的控制。 - 在 Spring Boot 中,通常主启动类上使用了
@SpringBootApplication,它包含了@ComponentScan,默认扫描主启动类所在包及其子包。
扫描过程:
- 扫描指定包:根据
basePackages或basePackageClasses确定的包路径,扫描类文件。 - 识别组件:通过检查类上的注解(如
@Component、@Service等)来识别组件。 - 注册 Bean 定义:将识别到的组件注册到 Spring 容器的 Bean 定义中。
示例说明:
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.example.app",
excludeFilters = @Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = Controller.class))
public class AppConfig {
}
这个配置类会扫描 com.example.app 包及其子包下除了被 @Controller 注解的类之外的所有组件。
到此这篇关于Spring Boot场景启动器(Starters)完全指南:从入门到精通的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring Boot场景启动器内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!


 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论