目录
- Java内省之Introspector
- Introspector使用不当导致内存泄露的风险
- IntrospectorCleanupListener
- Java内省Introspector应用
- IntroSpecor介绍
- 简单示例1
- 简单示例2::(编程客栈仅作参考)
Java内省之Introspector
在JavaBean规范中有如下描述:
大意是java默认情况下jdk使用低级的反射机制来分析Bean,为了方便其他人分析bean,java提供了一个内省类Introspector,使用Introspector的getBeanInfo方法可以获取一个封装了bean信息(包括属性和方法)的BeanInfo对象。
Introspector使用不当导致内存泄露的风险
框架几乎都使用了Introspector类来实现灵活性,但是Introspector在获取beanInfo对象时,为了提高性能使用了缓存保存beanInfo:
public static BeanInfo getBeanInfo(Class<?> beanClass)
throws IntrospectionException
{
if (!ReflectUtil.isPackageAccessible(beanClass)) {
return (new Introspector(beanClass, null, USE_ALL_BEANINFO)).getBeanInfo();
}
ThreadGroupContext context = ThreadGroupContext.getContext();
BeanInfo beanInfo;
synchronized (declaredMethodCache) {
android beanInfo = context.getBeanInfo(beanClass);
}
if (beanInfo == null) {
beanInfo = new Introspector(beanClass, null, USE_ALL_BEANINFO).getBeanInfo();
synchronized (declaredMethodCache) {
context.putBeanInfo(beanClass, beanInfo);
}
}
return beanInfo;
}
缓存使用ThreadGroupContext——线程组级别共享,类似与ThreadLocal。
内部使用WeakHashMap——key为弱引用来保存beanInfo,其中使用class作为key,beanInfo作为value。
同时使用WeakIdentityMap保存ThreadGroupContext对象(应该是ThreadGroupContext对象的hash值)与WeakHashMap的映射关系,也就是说不同线程组相互隔离:
final class ThreadGroupContext {
//WeakIdentityMap 判断key是否重复只判断hash是否相等,不调用equals
private static final WeakIdentityMap<ThreadGroupContext> contexts = new WeakIdentityMap<ThreadGroupContext>() {
protected ThreadGroupContext create(Object key) {
return new ThreadGroupContext();
}
};
/**
* Returns the appropriate {@code ThreadGroupContext} for the caller,
* as determined by its {@code ThreadGroup}.
*
* @return the application-dependent context
*/
static ThreadGroupContext getContext() {
return contexts.get(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup());
}
。
。
。
}
但是beanInfo中持有class对象,因此WeakHashMap的弱引用失效,Introspector提供了清除缓存的方法flushCaches。
但有些框架在使用Introspector之后并没有清除缓存
在spring中有如下描述:
/**
* Listener that flushes the JDK's {@link java.beans.Introspector JavaBeans Introspector}
* cache on web app shutdown. Register this listener in your {@code web.XML} to
* guarantee proper release of the web application class loader and its loaded classes.
*
* <p>If the JavaBeans Introspector has been used to analyze application classes,
* the system-level Introspector cache will hold a hard reference to those classes.
* Consequently, those classes and the web application class loader will not be
* garbage-collected on web app shutdown! This listener performs proper cleanup,
* to allow for garbage collection to take effect.
*
* <p>Unfortunately, the only way to clean up the Introspector is to flush
* the entire cache, as there is no way to specifically determine the
* application's classes referenced there. This will remove cached
* introspection results for all other applications in the server too.
*
* <p>Note that this listener is <i>not</i> necessary when using Spring's beans
* infrastructure within the application, as Spring's own introspection results
* cache will immediately flush an analyzed class from the JavaBeans Introspector
* cache and only hold a cache within the application's own ClassLoader.
*
* Although Spring itself does not create JDK Introspector leaks, note that this
* listener should nevertheless be used in scenarIOS where the Spring framework classes
* themselves reside in a 'common' ClassLoader (such as the system ClassLoader).
* In such a scenario, this listener will properly clean up Spring's introspection cache.
*
* <p>Application classes hardly ever need to use the JavaBeans Introspector
* directly, so are normally not the cause of Introspector resource leaks.
* Rather, many libraries and frameworks do not clean up the Introspector:
* e.g. Struts and Quartz.
*
* <p>Note that a single such Introspector leak will cause the entire web
* app class loader to not get garbage collected! This has the consequence that
* you will see all the application's static class resources (like singletons)
* around after web app shutdown, which is not the fault of those classes!
*
* <p>This listener should be registered as the first one in {@code web.xml},
* before any application listeners such as Spring's ContextLoaderListener.
*http://www.devze.com This allows the listener to take full effect at the right time of the lifecycle.
大意是在web应用中使用Introspector分析bean,当web应用停止时(这里应该指的是正常销毁,而非杀死进程暴力销毁),由于Introspector持有被分析bean的强引用,导致bean以及加载bean的classload无法被gc,造成内存泄露。
个人猜想,如果web应用停止之后,main方法运行结束,jvm退出应该不存在内存泄露的情况。但是,当web服务销毁之后main方法还在执行,那么就出现内存泄露。例如在一个tomcat中部署多个应用,在tomcat的manager App 页面关闭应用就会导致内存泄露。
大部分框架在创建线程池的时候都继承parentThreadGroup,因此即使使用WeakIdentityMap保存ThreadGroup对象的软引用与WeakHashMap的映射关系,但其他未关闭的web应用仍然持有ThreadGroup的强引用,因此WeakIdentityMap中的beanInfo缓存不会被回收——内存泄露。
IntrospectorCleanupListener
为了解决其他框架如:
Struts和Quartz(大部分博客均指出这两个框架使用Introspector后没有flushCaches,但我没有考证),一心为我们考虑的spring提供了解决方案 ——IntrospectorCleanupListener:
public class IntrospectorCleanupListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletConte开发者_开发培训xtEvent event) {
CachedIntrospectionResults.acceptClassLoader(Thread.currenthttp://www.devze.comThread().getContextClassLoader());
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
CachedIntrospectionResults.clearClassLoader(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
Introspector.flushCaches();
}
}
IntrospectorCleanupListener是servletContext的监听器,在servletContext销毁时,会执行contextDestroyed方法,调用Introspector.flushCaches(),防止内存泄露。
spring同时说明spring框架没有使用Introspector的缓存,而是使用Introspector分析bean之后,随即清理了Introspector缓存,并使用自己的缓存逻辑进行缓存,应该就是
CachedIntrospectionResults.acceptClassLoader(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader())
这行代码实现——未考证,因此spring声明在只使用spring框架时不需要考虑introspector导致内存泄露的问题。
但个人认为,如果某个框架在创建自己的线程池时,传入了新的ThreadGroup对象,那么IntrospectorCleanupListener 可能也无法工作。
Java内省Introspector应用
IntroSpecor介绍
内省(IntroSpector)是Java语言对JavaBean 类属性、事件的一种缺省处理方法。
例如类A中有属性name, 那我们可以通过getName,setName 来得到其值或者设置新的值。
通过getName/setName 来访问name属性,这就是默认的规则。
Java中提供了一套API 用来访问某个属性的getter/setter方法,通过这些API 可以使你不需要了解这个规则,这些API存放于包java.beans 中。
Class Diagram
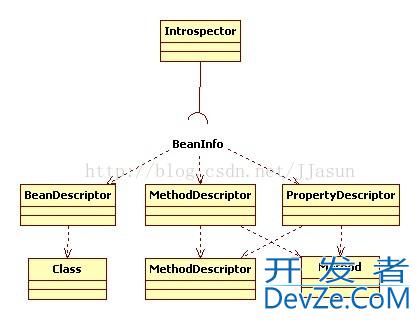
一般的做法是通过类Introspector的getBeanInfo方法获取某个对象的BeanInfo 信息,然后通过BeanInfo来获取属性的描述器(PropertyDescriptor),通过这个属性描述器就可以获取某个属性对应的getter/setter方法,然后我们就可以通过反射机制来调用这些方法。
我们又通常把javabean的实例对象称之为值对象(Value Object),因为这些bean中通常只有一些信息字段和存储方法,没有功能性方法。
一个JavaBean类可以不当JavaBean用,而当成普通类用。JavaBean实际就是一种规范,当一个类满足这个规范,这个类就能被其它特定的类调用。一个类被当作javaBean使用时,JavaBean的属性是根据方法名推断出来的,它根本看不到java类内部的成员变量。去掉set前缀,然后取剩余部分,如果剩余部分的第二个字母是小写的,则把剩余部分的首字母改成小的。
除了反射用到的类需要引入外,内省需要引入的类如下所示,它们都属于java.beans包中的类,自己写程序的时候也不能忘了引入相应的包或者类。
简单示例1
下面代码片断是设置某个JavaBean类某个属性的关键代码:
package com.jasun.test;
import java.beans.BeanInfo;
import java.beans.IntrospectionException;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils;
publicclass IntrospectorTest {
publi static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalArgumentException,
IntrospectionException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException {
UserInfo userInfo=new UserInfo("zhangsan", "123456");
String propertyName="userName";
Object retVal=getProperty(userInfo, propertyName);
System.out.println("retVal="+retVal); //retVal=zhangsan
Object value="abc";
setProperty(userInfo, propertyName, value);
retVal=getProperty(userInfo, propertyName);
System.out.println("retVal="+retVal); //retVal=abc
//使用BeanUtils工具包操作JavaBean
String userName=BeanUtils.getProperty(userInfo, propertyName);
System.out.println("userName="+userName);
Bewww.devze.comanUtils.setProperty(userInfo, propertyName, "linjiqin");
userName=BeanUtils.getProperty(userInfo, propertyName);
System.out.println("userName="+userName);
}
/**
* 设置属性
*
* @param clazz 对象名
* @param propertyName 属性名
* @param value 属性值
*/
private static void setProperty(Object clazz, String propertyName, Object value)
throws IntrospectionException,IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException{
//方法一
/*PropertyDescriptor pd=new PropertyDescriptor(propertyName, clazz.getClass());
Method methodSet=pd.getWriteMethod();
methodSet.invoke(clazz, value);*/
//方法二
BeanInfo beanInfo=Introspector.getBeanInfo(clazz.getClass());
PropertyDescriptor[] pds=beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
for(PropertyDescriptor pd:pds){
if(propertyName.equals(pd.getName())){
Method methodSet=pd.getWriteMethod();
methodSet.invoke(clazz, value);
break;
}
}
}
/**
* 获取属性
*
* @param clazz 对象名
* @param propertyName 属性名
* @return
* @throws IntrospectionException
* @throws InvocationTargetException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
*/
private static Object getProperty(Object clazz, String propertyName)
throws IntrospectionException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException{
//方法一
/*PropertyDescriptor pd=new PropertyDescriptor(propertyName, clazz.getClass());
Method methodGet=pd.getReadMethod();
return methodGet.invoke(clazz);*/
//方法二
Object retVal=null;
BeanInfo beanInfo=Introspector.getBeanInfo(clazz.getClass());
PropertyDescriptor[] pds=beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
for(PropertyDescriptor pd:pds){
if(propertyName.equals(pd.getName())){
Method methodGet=pd.getReadMethod();
retVal=methodGet.invoke(clazz);
break;
}
}
return retVal;
}
}
UserInfo类
package com.ljq.test;
publicclass UserInfo {
private String userName;
private String pwd;
public UserInfo(String userName, String pwd) {
super();
this.userName = userName;
this.pwd = pwd;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
publicvoid setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
publicvoid setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
}
简单示例2::(仅作参考)
package com.siyuan.jdktest;
import java.beans.BeanDescriptor;
import java.beans.BeanInfo;
import java.beans.IntrospectionException;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.MethodDescriptor;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
/**
* @return the age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* @param age the age to set
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
/**
* @return the name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* @param name the name to set
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class IntrospectorTest {
/**
* @param args
* @throws IntrospectionException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IntrospectionException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Person.class);
System.out.println("BeanDescriptor===========================================");
BeanDescriptor beanDesc = beanInfo.getBeanDescriptor();
Class cls = beanDesc.getBeanClass();
System.out.println(cls.getName());
System.out.println("MethodDescriptor===========================================");
MethodDescriptor[] methodDescs = beanInfo.getMethodDescriptors();
for (int i = 0; i < methodDescs.length; i++) {
Method method = methodDescs[i].getMethod();
System.out.println(method.getName());
}
System.out.println("PropertyDescriptor===========================================");
PropertyDescriptor[] propDescs = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
for (int i = 0; i < propDescs.length; i++) {
Method methodR = propDescs[i].getReadMethod();
if (methodR != null) {
System.out.println(methodR.getName());
}
Method methodw = propDescs[i].getWriteMethod();
if (methodW != null) {
System.out.println(methodW.getName());
}
}
}
}
运行结果
BeanDescriptor===========================================
com.siyuan.jdktest.PersonMethodDescriptor===========================================hashCodesetAgeequalswaitwaitnotifygetClasstoStringgetAgenotifyAllsetNamewaitgetNamePropertyDescriptor===========================================getAgesetAgegetClassgetNamesetName
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。


 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论