目录
- 一、条件注解@Conditional
- 二、条件判断接口Condition
- 1. ConditionContext
- 2. AnnotatedTypeMetadata
- 三、@Conditional如何被解析,Condition方法何时调用?
- 四、典型应用 @Profile
一、条件注解@Conditional
@Conditional是Spring4.0提供的一个用于条件装配的注解,其定义了一个Condition的数组,只有当数组所有的条件都满足的时候,组件才会被导入容器。
/**
* Indicates that a component is only eligible for registration when all
* {@linkplain #value specified conditions} match.
*
* <p>A <em>condition</em> is any state that can be determined programmatically
* before the bean definition is due to be registered (see {@link Condition} for details).
*
* <p>The {@code @Conditional} annotation may be used in any of the following ways:
* <ul>
* <li>as a type-level annotation on any class directly or indirectly annotated with
* {@code @Component}, including {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes</li>
* <li>as a meta-annotation, for the purpose of composing custom stereotype
* annotations</li>
* <li>as a method-level annotation on any {@link Bean @Bean} method</li>
* </ul>
*
* <p>If a {@code @Configuration} class is marked with {@code @Conditional},
* all of the {@code @Bean} methods, {@link Import @Import} annotations, and
* {@link ComponentScan @ComponentScan} annotations associated with that
* class will be subject to the conditions.
*
* <p><strong>NOTE</strong>: Inheritance of {@code @Conditional} annotations
* is not supported; any conditions from superclasses or from overridden
* methods will not be considered. In order to enforce these semantics,
* {@code @Conditional} itself is not declared as
* {@link Java.lang.annotation.Inherited @Inherited}; furthermore, any
* custom <em>composed annotation</em> that is meta-annotated with
* {@code @Conditional} must not be declared as {@code @Inherited}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 4.0
* @see Condition
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Conditional {
/**
* All {@link Condition}s that must {@linkplain Condition#matches match}
* in order for the component to be registered.
*/
Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
}
@Conditional注解可以有两种使用方法:
- 类型级别,任意直接或者间接标注了@Conponent注解的类或者注解,比如@Configuration或者@Profile
- 方法级别,任意标注了@Bean注解的方法
如果一个@Configuration类标注了@Conditional,那么这个类所有的@Bean方法,@ComponentScan和@Import的结果都受@Conditional注解的条件约束。 特别要注意的是:@Conditional是不支持继承的,任何父类的条件注解或者方法继承的条件注解都不会生效。为了强化这些语义,@Conditional本身并没有标注@Inherited。另外,任何使用了@Conditional注解的组合注解都不能声明为@Inherited。
二、条件判断接口Condition
@Conditional注解依赖于Condition接口,该接口提供真正的条件判断逻辑。
/**
* A single {@code condition} that must be {@linkplain #matches matched} in order
* for a component to be registered.
*
* <p>Conditions are checked immediately before the bean-definition is due to be
* registered and are free to veto registration based on any criteria that can
* be determined at that point.
*
* <p>Conditions must follow the same restrictions as {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor}
* and take care to never interact with bean instances. For more fine-grained control
* of conditions that interact with {@code @Configuration} beans consider the
* {@link ConfigurationCondition} interface.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 4.0
* @see ConfigurationCondition
* @see Conditional
* @see ConditionContext
*/
public interface Condition {
/**
* Determine if the condition matches.
* @param context the condition context
* @param metadata metadata of the {@link org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata class}
* or {@link org.springframework.core.type.MethodMetadata method} being checked.
* @return {@code true} if the condition matches and the component can be registered
* or {@code false} to veto registration.
*/
boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata);
}
Condition接口传递两个参数ConditionContext和AnnotatedTypeMetadata,在Condition实现类中可以直接使用这两个参数,获取环境、容器、类等相关信息。
1. ConditionContext
/**
* Context information for use by {@link Condition}s.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 4.0
*/
public interface ConditionContext {
/**
* Return the {@link BeanDefinitionRegistry} that will hold the bean definition
* should the condition match or {@code null} if the registry is not available.
* @return the registry or {@code null}
*/
BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry();
/**
* Return the {@link ConfigurableListableBeanFactory} that will hold the bean
* definition should the condition match or {@code null} if the bean factory
* is not available.
* @return the bean factory or {@code null}
*/
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory();
/**
* Return the {@link Environment} for which the current application is running
* or {@code null} if no environment is available.
* @return the environment or {@code null}
*/
Environment getEnvironment();
/**
* Return the {@link ResourceLoader} currently being used or {@code null}
* if the resource loader cannot be obtained.
* @return a resource loader or {@code null}
*/
ResourceLoader getResourceLoader();
/**
* Return the {@link ClassLoader} that should be used to load additional
* classes or {@code null} if the default classloader should be used.
* @return the class loader or {@code null}
*/
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
CondtitionContext可以获取到BeanDefinitionRegistry、ConfigurableListableBeanFactory、Environment、ResourceLoader、ClassLoader这些环境相关的信息。
2. AnnotatedTypeMetadata
public interface AnnotatedTypeMetadata {
// 根据“全类名”判断是否被指定 直接注解或元注解 标注
booleandroidan isAnnotated(String annotationName);
// 根据”全类名“获取所有注解属性(包括元注解)
@Nullable
Map<String, Object> getAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName);
@Nullable
// 同上,但是第二个参数传 true 时会把属性中对应值为 Class 的值
// 转为 字符串,避免需要预先加载对应 Class
Map<String, Object> getAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName, boolean classValuesAsString);
@Nullable
// 同上,MultiValueMap 是一个 key 可以对应多个 value 的变种 map
MultiValueMap<String, Object> getAllAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName);
@Nullable
MultiValueMap<String, Object> getAllAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName, boolean classValuesAsString);
}
顶层接口,可被注解标注类型(类、方法)元数据的抽象,提供了两个核心方法:
- 根据 全类名 判断是否被指定注解标注
- 根据 全类名 返回指定注解的属性集合(包括元注解)
三、@Conditional如何被解析,Condition方法何时调用?
@Conditional和Condition的相关逻辑是在类ConditionEvaLuator#中实现的。
class ConditionEvaluator {
private final ConditionContextImpl context;
/**
* Create a new {@link ConditionEvaluator} instance.
*/
public ConditionEvaluator(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.context = new ConditionContextImpl(registry, environment, resourceLoader);
}
/**
* Determine if an item should be skipped based on {@code @Conditional} annotations.
* The {@link ConfigurationPhase} will be deduced from the type of item (i.e. a
* {@code @Configuration} class will be {@link ConfigurationPhase#PARSE_CONFIGURATION})
* @param metadata the meta data
* @return if the item should be skipped
*/
public boolean shouldSkip(AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
return shouldSkip(metadata, null);
}
/**
* Determine if an item should be skipped based on {@code @Conditional} annotations.
* @param metadata the meta data
* @param phase the phase of the call
* @return if the item should be skipped
*/
public boolean shouldSkip(AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, ConfigurationPhase phase) {
if (metadata == null || !metadata.isAnnotated(Conditional.class.getName())) {
return false;
}
if (phase == null) {
if (metadata instanceof AnnotationMetadata &&
ConfigurationClassUtils.isConfigurationCandidate((AnnotationMetadata) metadata)) {
return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION);
}
return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN);
}
List<Condition> conditions = new ArrayList<Condition>();
for (String[] conditionClasses : getConditionClasses(metadata)) {
for (String conditionClass : conditionClasses) {
Condition condition = getCondition(conditionClass, this.context.getClassLoader());
conditions.add(condition);
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(conditions);
for (Condition condition : conditions) {
ConfigurationPhase requiredPhase = null;
if (condition instanceof ConfigurationCondition) {
requiredPhase = ((ConfigurationCondition) condition).getConfigurationPhase();
}
if (requiredPhase == null || requiredPhase == phase) {
if (!condition.matches(this.context, metadata)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private List<String[]> getConditionClasses(AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
MultiValueMap<String, Object> attributes = metadata.getAllAnnotationAttributes(Conditional.class.getName(), true);
Object values = (attributes != null ? attributes.get("value") : null);
return (List<String[]>) (values != null ? values : Collections.emptyList());
}
private Condition getCondition(String conditionClassName, ClassLoader classloader) {
Class<?> conditionClass = ClassUtils.resolveClassName(conditionClassName, classloader);
return (Condition) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(conditionClass);
}
/**
* Implementation of a {@link ConditionContext}.
*/
private static class ConditionContextImpl implements ConditionContext {
private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
private final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
private final Environment environment;
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
public ConditionContextImpl(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.registry = registry;
this.beanFactory = deduceBeanFactory(registry);
this.environment = (environment != null ? environment : deduceEnvironment(registry));
this.resourceLoader = (resourceLoader != null ? resourceLoader : deduceResourceLoader(registry));
}
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory deduceBeanFactory(BeanDefinitionRegistry source) {
if (source instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
return (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) source;
}
if (source instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
return (((ConfigurableApplicationContext) source).getBeanFactory());
}
return null;
}
private Environment deduceEnvironment(BeanDefinitionRegistry source) {
if (source instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
return ((EnvironmentCapable) source).getEnvironment();
}
return null;
}
private ResourceLoader deduceResourceLoader(BeanDefinitionRegistry source) {
if (source instanceof ResourceLoader) {
return (ResourceLoader) source;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public BeajavascriptnDefinitiohttp://www.devze.comnRegistry getRegistry() {
return this.registry;
}
@Override
public ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
return this.beanFactory;
}
@Override
public Environment getEnvironment() {
return this.environment;
}
@Override
public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() {
return this.resourceLoader;
}
@Override
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
return this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader();
}
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
return this.beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader();
}
return null;
}
}
}
而该类根据构造方法的调用点,可知以下几个类会使用到。
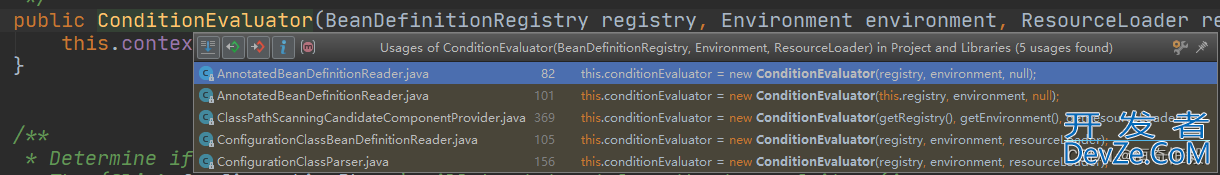
- AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 注解标注时候
- ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider注解扫描时候
- ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader、ConfigurationClassParser(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor) 解析Chttp://www.devze.comonfiguration注解的过程中
四、典型应用 @Profile
@Profile就是典型地基于@Conditional的扩展,其条件逻辑封装在ProfileCondition中
class ProfileCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
if (context.getEnvironment() != null) {
MultiValueMap<String, Object> attrs = metadata.getAllAnnotationAttributes(Profile.class.getName());
if (attrs != null) {
for (Object value : attrs.get("value")) {
if (context.getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(((String[]) valuejs))) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
Springboot中的应用
到此这篇关于SpringBoot条件注解@Conditional详细解析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot条件注解@Conditional内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!

 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论