目录
- 1.Pip install nuitka安装
- 2.nuitka yanhua.py打包
- 3.执行exe程序
- 4.添加参数打包
- Nuitka对更复杂的GUI程序和第三方库支持情况
- 总结
目前python打包成exe的工具主要有:PyInstaller Briefcase py2exe py2app Nuitka CX_Freeze等。
不同于C++代码,可以直接编译成可执行的exe文件,或者js代码在浏览器中就能执行,python代码必须通过python解释器来运行,很多操作系统都没有预装。所以需要通过工具将python代码打包成可独立运行的exe文件,工具主要包括PyTnstaller Briefcase py2exe py2app Nuitka CX_Freeze等,本期介绍打包工具Nuitka。
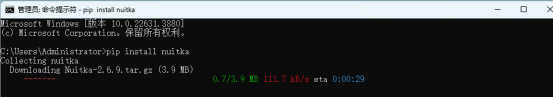
1.Pip install nuitka安装
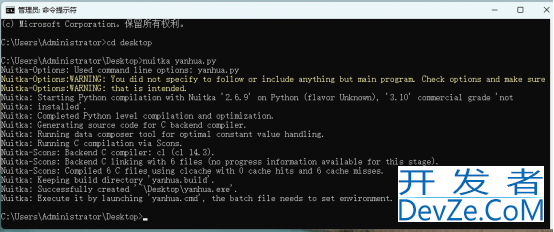
2.nuitka yanhua.py打包
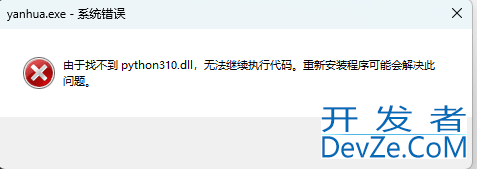
3.执行exe程序
发现直接打包好的exe文件仍然不可以在没有安装python的电脑上执行
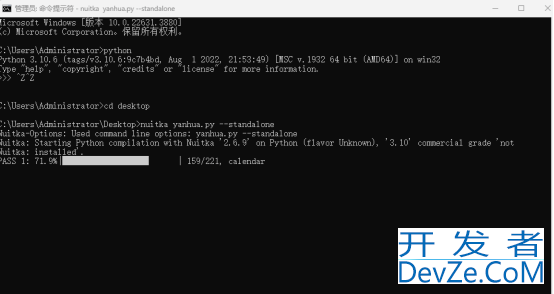
4.添加参数打包
所以我们还得再打包时加上参数 --standalone,这样才会将python解释器和目标代码的所有依赖都打包进去,参数--onefile将所有文件打包成一个单独运行的可执行文件
打包完成

一般默认的cl编译,也可以添加mingw编译。
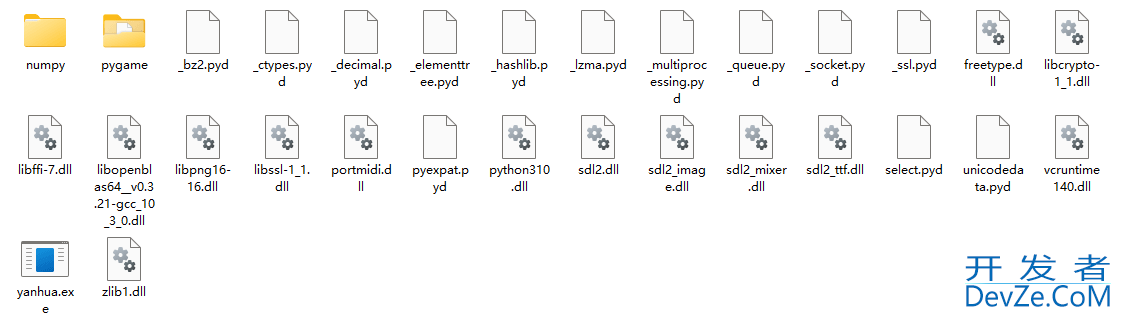
打包可能出现以下情况,可能是微信开发者工具中ws2_32.dll导致的问题,直接卸载微信开发者工具就好了。
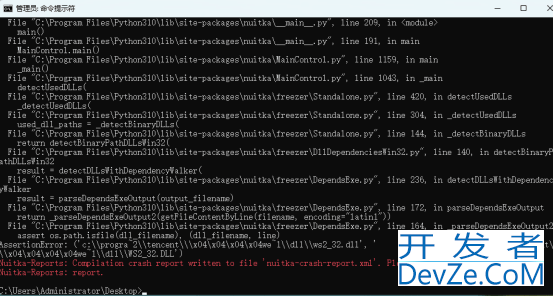
Nuitka对更复杂的GUI程序和第三方库支持情况
以下是一个示例代码
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk, messagebox, filedialog
import os
class MyApp:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("功能演示程序")
self.root.iconbitmap("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/z.ico")
self.root.geometry("800x600")
# 创建选项卡
self.notebook = ttk.Notebook(root)
self.notebook.pack(expand=True, fill='both', padx=5, pady=5)
# 创建三个选项卡页面
self.tab1 = ttk.Frame(self.notebook)
self.tab2 = ttk.Frame(self.notebook)
self.tab3 = ttk.VxBDtFrame(self.notebook)
self.notebook.add(self.tab1, text='文本处理')
self.notebook.add(self.tab2, text='文件操作')
self.notebook.add(self.tab3, text='计算工具')
self.setup_text_tab()
self.setup_file_tab()
self.setup_calc_tab()
# 创建状态栏
self.status_bar = tk.Label(root, text="就绪", bd=1, relVxBDtief=tk.SUNKEN, anchor=tk.W)
self.status_bar.pack(side=tk.BOTTOM, fill=tk.X)
def setup_text_tab(self):
# 文本输入区域
frame = ttk.LabelFrame(self.tab1, text="文本处理区域", padding=10)
frame.pack(fill='both', expand=True, padx=5, pady=5)
self.text_input = tk.Text(frame, height=10)
self.text_input.pack(fill='both', expand=True, pady=5)
btn_frame = ttk.Frame(frame)
btn_frame.pack(fill='x', pady=5)
ttk.Button(btn_frame, text="转大写", command=self.convert_upper).pack(side='left', padx=5)
ttk.Button(btn_frame, text="转小写", command=self.convert_lower).pack(side='left', padx=5)
ttk.Button(btn_frame, text="清空", command=self.clear_text).pack(side='left', padx=5)
ttk.Button(btn_frame, text="字数统计", command=self.count_words).pack(side='left', padx=5)
def setup_file_tab(self):
frame = ttk.LabelFrame(self.tab2, text="文件操作", padding=10)
frame.pack(fill='both', expand=True,编程 padx=5, pady=5)
ttk.Button(frame, text="选择文件", command=self.select_file).pack(pady=5)
self.file_label = ttk.Label(frame, text="未选择文件")
self.file_label.pack(pady=5)
self.file_content = tk.Text(frame, height=10)
self.file_content.pack(fill='both', expand=True, pady=5)
ttk.Button(frame, text="保存内容", command=self.save_file).pack(pady=5)
def setup_calc_tab(self):
frame = ttk.LabelFrame(self.tab3, text="简单计算器", padding=10)
frame.pack(fill='both', expand=True, padx=5, pady=5)
# 输入框
input_frame = ttk.Frame(frame)
input_frame.pack(fill='x', pady=5)
ttk.Label(input_frame, text="数字1:").pack(side='left')
self.num1 = ttk.Entry(input_frame, width=10)
self.num1.pack(side='left', padx=5)
ttk.Label(input_frame, text="数字2:").pack(side='left')
self.num2 = ttk.Entry(input_frame, width=10)
self.num2.pack(side='left', padx=5)
# 计算按钮
btn_frame = ttk.Frame(frame)
btn_frame.pack(fill='x', pady=5)
ttk.Button(btn_frame, text="+", command=lambda: self.calculate('+')).pack(side='left', padx=5)
ttk.Button(btn_frame, text="-", command=lambda: self.calculate('-')).pack(side='left', padx=5)
ttk.Button(btn_frame, text="", command=lambda: self.calculate('*')).pack(side='left', padx=5)
ttk.Button(btn_frame, text="", command=lambda: self.calculate('/')).pack(side='left', padx=5)
# 结果显示
self.result_label = ttk.Label(frame, text="结果: ")
self.result_label.pack(pady=5)
# 文本处理功能
def convert_upper(self):
text = self.text_input.get("1.0", tk.END)
self.text_input.delete("1.0", tk.END)
self.text_input.insert("1.0", text.upper())
self.status_bar.config(text="文本已转换为大写")
def convert_lower(self):
text = self.text_input.get("1.0", tk.END)
self.text_input.delete("1.0", tk.END)
self.text_input.insert("1.0", text.lower())
self.status_bar.config(text="文本已转换为小写")
def clear_text(self):
self.text_input.delete("1.0", tk.END)
self.status_bar.config(text="文本已清空")
def count_words(self):
text = self.text_input.get("1.0", tk.END).strip()
words = len(text.split())
chars = len(text)
messagebox.showinfo("统计结果", f"字数统计:\n单词数:{words}\n字符数:{chars}")
# 文件操作功能
def select_file(self):
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename()
if file_path:
self.file_label.config(t编程ext=file_path)
try:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
content = file.read()
self.file_content.delete("1.0", tk.END)
self.file_content.insert("1.0", content)
self.status_bar.config(text=f"已打开文件:{os.path.basename(file_path)}")
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("错误", f"无法打开文件:{str(e)}")
def save_file(self):
file_path = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(defaultextension=".txt")
if file_path:
try:
content = self.file_content.get("1.0", tk.END)
with open(file_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(content)
self.status_bar.config(text=f"文件已保存:{os.path.basename(file_path)}")
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("错误", f"保存失败:{str(e)}")
# 计算器功能
def calculate(self, operator):
try:
num1 = float(self.num1.get())
num2 = float(self.num2.get())
if operator == '+':
result = num1 + num2
elif operator == '-':
result = num1 - num2
elif operator == '*':
result = num1 * num2
VxBDt elif operator == '/':
if num2 == 0:
raise ValueError("除数不能为零")
result = num1 / num2
self.result_label.config(text=f"结果: {result:.2f}")
self.status_bar.config(text="计算完成")
except ValueError as e:
messagebox.showerror("错误", str(e))
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("错误", "请输入有效的数字")
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = tk.Tk()
app = MyApp(root)
root.mainloop()
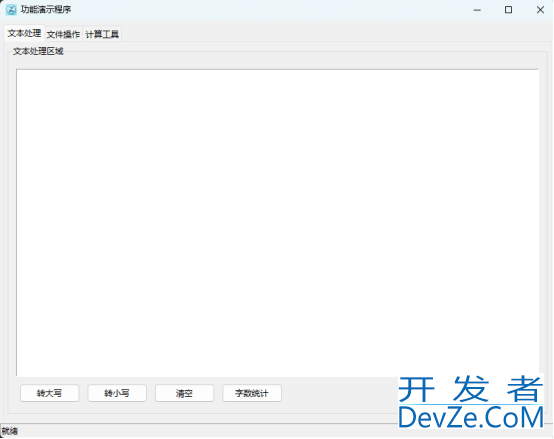
程序运行界面如下图
打包
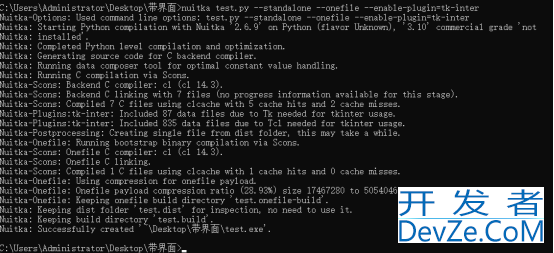

在test.list中可以看到打包好的依赖项,执行exe,如下图,正常运行。

总结
不同于其他打包工具,nuitka是将python代码,转换成C代码,在通过C编译器编译成可执行文件。
优势:支持外部资源,支持Windows、linux、以及MACOS系统。打Nuitka --help可以查看所有命令参数。
到此这篇关于python中nuitka使用程序打包的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python nuitka程序打包内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!

 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论