目录
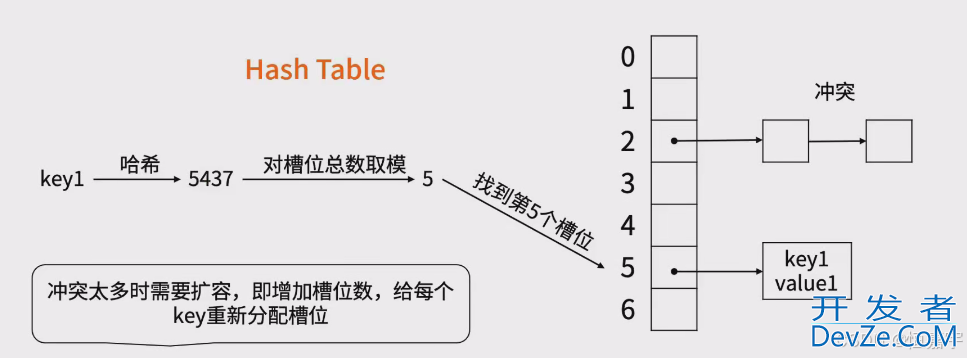
- HashMap是一种基于哈希表实现的键值对存储结构,它通过哈希函数将键映射到数组的索引位置,支持高效的插入、查找和删除操作。其核心原理如下:
- 哈希函数:将键转换为数组索引。理想情况下,不同键应映射到不同索引,但冲突难以避免。
- 数组+链表:使用数组作为桶(Bucket),每个桶是一个链表,解决哈希冲突(链地址法)。
- 动态扩容:当元素数量超过容量与负载因子的乘积时,扩容并重新分配元素,保持操作高效性。
package main
import "fmt"
// Entry 键值对链表节点
type Entry struct {
Key string
Value interface{}
Next *Entry
}
// HashMap 哈希表结构
type HashMap struct {
buckets []*Entry // 桶数组
capacity int // 初始容量
size int // 元素数量
loadFactor float64 // 负载因子
}
// NewHashMap 初始化哈希表
func NewHashMap(capacity int) *HashMap {
return &HashMap{
buckets: make([]*Entry, capacity),
capacity: capacity,
loadFactor: 0.75,
}
}
// hash 哈希函数(FNV-1a算法)
func (h *HashMap) hash(key string) int {
const (
offset = 2166136261
prime = 16777619
)
hash := offset
for _, c := range key {
hash ^= int(c)
hash *= prime
}
return hash
}
// getIndex 计算键对应的桶索引
func (h *HashMap) getIndex(key string) int {
return h.hash(key) % h.capacity
}
// Put 插入键值对
func (h *HashMap) Put(key string, value interface{}) {
if float64(h.size)/float64(h.capacity) >= jsh.loadFactor {
h.resize()
}
index := h.getIndex(key)
entry := h.bucZvFuRkets[index]
// 遍历链表查找键是否存在
for entry != nil {
if entry.Key == key {
entry.Value = value // 存在则更新
return
}
entry = entry.Next
}
// 不存在则插入链表头部
h.buckets[index] = &Entry{
Key: key,
Value: value,
Next: h.buckets[index],
}
h.size++
}
// Get 获取值
func (h *HashMap) Get(key string) (interface{}, bool) {
index := h.getIndex(key)
entry := h.buckets[index]
for entry != nil {
if entry.Key == key {
return entry.Value, t编程rue
}
entry = entry.Next
}
return nil, false
}
// Delete 删除键
func (h *HashMap) Delete(key string) bool {
index := h.getIndex(key)
entry := h.buckets[index]
var prpythonev *Entry
for entry != nil {
if entry.Key == key {
if prev == nil {
h.buckets[index] = entry.Next // 删除头节点
} else {
prev.Next = entry.Next // 中间或尾部节点
}
编程 h.size--
return true
}
prev = entry
entry = entry.Next
}
return false
}
// resize 扩容哈希表
func (h *HashMap) resize() {
newCapacity := h.capacity * 2
newBuckets := make([]*Entry, newCapacity)
for i := 0; i < h.capacity; i++ {
entry := h.buckets[i]
for entry != nil {
next := entry.Next
newIndex := h.hash(entry.Key) % newCapacity // 重新计算索引
entry.Next = newBuckets[newIndex] // 插入新桶头部
newBuckets[newIndex] = entry
entry = next
}
}
h.buckets = newBuckets
h.capacity = newCapacity
}
func main() {
hm := NewHashMap(2) // 初始容量设为2便于触发扩容
hm.Put("name", "Alice")
hm.Put("age", 30)
hm.Put("lang", "Go") // 触发扩容
if val, ok := hm.Get("name"); ok {
fmt.Println("name:", val) // 输出 Alice
}
hm.Delete("age")
if _, ok := hm.Get("age"); !ok {
fmt.Println("age deleted") // 输出此句
}
}
到此这篇关于golang HashMap实现原理的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关goland hashmap原理内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!



 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论